Difference between revisions of "Lab 5 TF EIM"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=The LC cicuit= | =The LC cicuit= | ||
[[File:TF_EIM_Lab5_LC.png| 200 px]] | [[File:TF_EIM_Lab5_LC.png| 200 px]] | ||
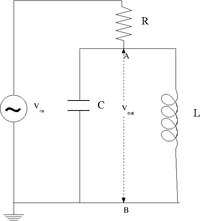
| − | #Design a '''parallel''' LC resonant circuit with a resonant frequency between 50-200 kHz. use <math>L</math> = 10 - 100 <math>\mu H</math>, R = 1k <math>\Omega</math>. | + | #Design a '''parallel''' LC resonant circuit with a resonant frequency between 50-200 kHz. use <math>L</math> = 10 - 100 <math>\mu H</math>, R = 1k <math>\Omega</math> (Note <math>R_L</math> is the inherent resistance of the inductor). |
#Construct the LC circuit using a non-polar capacitor | #Construct the LC circuit using a non-polar capacitor | ||
#Measure the Gain <math>\equiv \frac{V_{out}}{V_{in}}</math> as a function of frequency when r=0. (20 pnts) | #Measure the Gain <math>\equiv \frac{V_{out}}{V_{in}}</math> as a function of frequency when r=0. (20 pnts) | ||
Revision as of 04:32, 2 February 2011
LC Resonance circuits
The LC cicuit
- Design a parallel LC resonant circuit with a resonant frequency between 50-200 kHz. use = 10 - 100 , R = 1k (Note is the inherent resistance of the inductor).
- Construct the LC circuit using a non-polar capacitor
- Measure the Gain as a function of frequency when r=0. (20 pnts)
- Measure the Gain when an external resistance (r) approximately equals to the inherent resistance of the rf choke . (20 pnts)
- Compare the measured and theoretical values of the resonance frequency () (10 pnts)
Questions
- If r=0, show that . (10 pnts)
- Show that at resonance. (10 pnts)
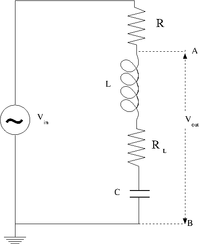
The RLC cicuit
- Design and construct a series LRC circuit.
- Measure and Graph the Gain as a function of the oscillating input voltage frequency. (20 pnts)
Questions
- What is the current at resonance? (5 pnts)
- What is the current as ? (5 pnts)