Difference between revisions of "Forest IonizationChambers"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| − | = | + | = Recombination= |
| + | Until the voltage reaches a high enough value (threshold), the liberated electrons produces will recombine with the gas before reaching the wire. | ||
| + | =Ionization= | ||
| + | |||
| + | Once the voltage is increased beyond the above threshold, the ions/ electrons make it to the cathode/anode and produce an electronic pulse on the wire (cathode). | ||
| + | |||
| + | quick definitions | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Anode | ||
| + | : Current IN, positively charged electrode | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Cathode | ||
| + | :Current OUT, negatively charged electrode | ||
| + | |||
| + | The flow of electrons is from the cathode to the anode. Current is defined as the opposite direction to the electron flow. | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 9 June 2008
An ionization chamber is essentially a gas filled volume which has one or more wires suspended inside with a voltage bias used to collect any ions or liberated electrons within the volume.
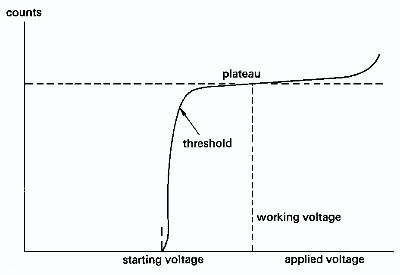
There are 4 basic operating regions which are determined by the amount of the voltage across the wire(s).
- recombination
- ionization
- proportional (plataue)
- Geiger-Muller
Recombination
Until the voltage reaches a high enough value (threshold), the liberated electrons produces will recombine with the gas before reaching the wire.
Ionization
Once the voltage is increased beyond the above threshold, the ions/ electrons make it to the cathode/anode and produce an electronic pulse on the wire (cathode).
quick definitions
- Anode
- Current IN, positively charged electrode
- Cathode
- Current OUT, negatively charged electrode
The flow of electrons is from the cathode to the anode. Current is defined as the opposite direction to the electron flow.