Difference between revisions of "2NCorr SPDP Introduction"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
For two-neutron opening angle (<math>\theta_{nn}</math>) measurements, the control distribution is made by examining neutron events from pairs of two different pulses. The pairs are chosen such that the pulses occurred within fewer than a couple 100 ms of each other , in order to ensure that they were subject to the same experimental conditions, thereby avoiding the side effects of time varying factors like the drifting of beam current and high voltage. If, for any given pulse pair, there is a neutron event in both pulses, then the opening angle between the two events is calculated. Since no information can be shared between the neutrons of different pulses, this distribution is free of any two-neutron correlations. | For two-neutron opening angle (<math>\theta_{nn}</math>) measurements, the control distribution is made by examining neutron events from pairs of two different pulses. The pairs are chosen such that the pulses occurred within fewer than a couple 100 ms of each other , in order to ensure that they were subject to the same experimental conditions, thereby avoiding the side effects of time varying factors like the drifting of beam current and high voltage. If, for any given pulse pair, there is a neutron event in both pulses, then the opening angle between the two events is calculated. Since no information can be shared between the neutrons of different pulses, this distribution is free of any two-neutron correlations. | ||
| − | On an individual neutron basis, the set of events from same pulses and different pulses are indistinguishable, thus both are influenced by detector geometry and efficiency in the exact same way. So barring two-neutron correlations and a scaling factor, the | + | On an individual neutron basis, the set of events from same pulses (SP) and different pulses (DP) are indistinguishable, thus both are influenced by detector geometry and efficiency in the exact same way. So barring two-neutron correlations and a scaling factor, the DP distribution is identical to the SP distribution, making it a good choice for a normalizing distribution. |
| + | |||
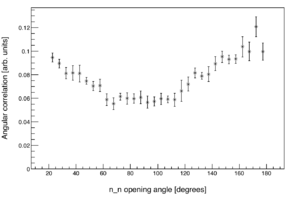
Here, the words "angular correlation" refer to the <math>\theta_{nn}</math> rate relative to a completely uncorrelated neutron source formed by pairing neutron events across separate pulses. The plot to the right shows the same data from the plot above after normalization. | Here, the words "angular correlation" refer to the <math>\theta_{nn}</math> rate relative to a completely uncorrelated neutron source formed by pairing neutron events across separate pulses. The plot to the right shows the same data from the plot above after normalization. | ||
Revision as of 00:34, 22 January 2018
The calculation of angular correlation
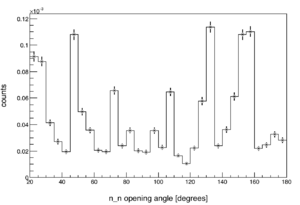
The efficiency and acceptance of the neutron detector array varies chaotically over the range of opening angles (see figure to the right). This is in part due to the detector array's non-spherical symmetry, and also to its varying detection efficiency as a function of both particle position and energy.
For this reason, in order to produce meaningful results, each distribution must be normalized by a "control" distribution. This normalization is done by diving the values of a distribution by the control distribution on a bin-by-bin basis. A control distribution should be virtually identical to the measured distribution, only except that is lacks the correlations of interest, and so when dividing the two distributions, all other effects cancel.
.
Same pulse and different pulse distributions
For two-neutron opening angle () measurements, the control distribution is made by examining neutron events from pairs of two different pulses. The pairs are chosen such that the pulses occurred within fewer than a couple 100 ms of each other , in order to ensure that they were subject to the same experimental conditions, thereby avoiding the side effects of time varying factors like the drifting of beam current and high voltage. If, for any given pulse pair, there is a neutron event in both pulses, then the opening angle between the two events is calculated. Since no information can be shared between the neutrons of different pulses, this distribution is free of any two-neutron correlations. On an individual neutron basis, the set of events from same pulses (SP) and different pulses (DP) are indistinguishable, thus both are influenced by detector geometry and efficiency in the exact same way. So barring two-neutron correlations and a scaling factor, the DP distribution is identical to the SP distribution, making it a good choice for a normalizing distribution.
Here, the words "angular correlation" refer to the rate relative to a completely uncorrelated neutron source formed by pairing neutron events across separate pulses. The plot to the right shows the same data from the plot above after normalization.
.
single-neutron and using Cf252 for normalization
Another measurement possible with this set up, is the distribution of the angle between neutron singles, and the direction of the incident photon beam (). When constructing a distribution from neutron singles, the method of using uncorrelated neutron pairs from different pulses no longer works, because while the neutrons in a pair are uncorrelated with each other, they are both correlated with the direction of the incident photon beam. For this reason, neutron singles from the spontaneous fission (SF) of Cf252 are used for normalization. This choice leads to several issues, because there are differences in experimental conditions between the measurement of photo-neutrons in the presence of a photon beam, versus the measurement of neutrons from the SF of Cf252. The energy spectrum of neutrons from Cf252 differ from that of our photo-neutrons. During the Cf252 measurement, the detectors experience much dead-time caused by the detection of photons. Also, the noise profiles are very different. Each of these effects must be removed or neglected by employing various corrections and assumptions, which results in a analysis procedure that is less robust than the same-pulse different-pulse method.
Accidentals and trues
An accidental neutron coincidence, or accidental for short, is defined here as any pair of neutrons that are uncorrelated despite having been produced during the same pulse. For example, a neutron from a (gamma,n) reaction paired with a neutron from a (gamma, fiss) reaction. As another example, consider a pulse which causes two photofission events, such that one fission releases four and the other two correlated neutrons, creating 4*2=8 possible distinct pairs of uncorrelated neutrons, or in other words, eight accidentals.
A true neutron coincidence, or true for short, is defined here as any pair correlated neutrons from the same pulse. For example, a photofission event that produces 4 correlated neutrons, creates (4*3)/2=6 trues.
Throughout the experiment, measured trues/accidentals always occurred as two-neutron coincidences, as there were never three or more neutrons detected in coincidence.