Difference between revisions of "Wire angle correspondance"
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
|+ Table 1: Superlayer 1 Wire 1 Coordinates | |+ Table 1: Superlayer 1 Wire 1 Coordinates | ||
|- style="font-weight:bold; text-align:center;" | |- style="font-weight:bold; text-align:center;" | ||
| − | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"| | + | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Coordinates(cm) |
! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 1 | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 1 | ||
! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 2 | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 2 | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
|+ Table 1: Superlayer 1 Wire 2 Coordinates | |+ Table 1: Superlayer 1 Wire 2 Coordinates | ||
|- style="font-weight:bold; text-align:center;" | |- style="font-weight:bold; text-align:center;" | ||
| − | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"| | + | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Coordinates(cm) |
! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 1 | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 1 | ||
! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 2 | ! style=" border:1px solid gray;"|Layer 2 | ||
Revision as of 19:06, 30 November 2016
Determining wire-theta correspondence
To associate the hits with the Moller scattering angle theta, the occupancy plots of the drift chamber hits by means of wire numbers and layer must be translated using the physical constraints of the detector. Using the data released for the DC:
DC: Drift Chambers(specs)
DC Geometry(geom)
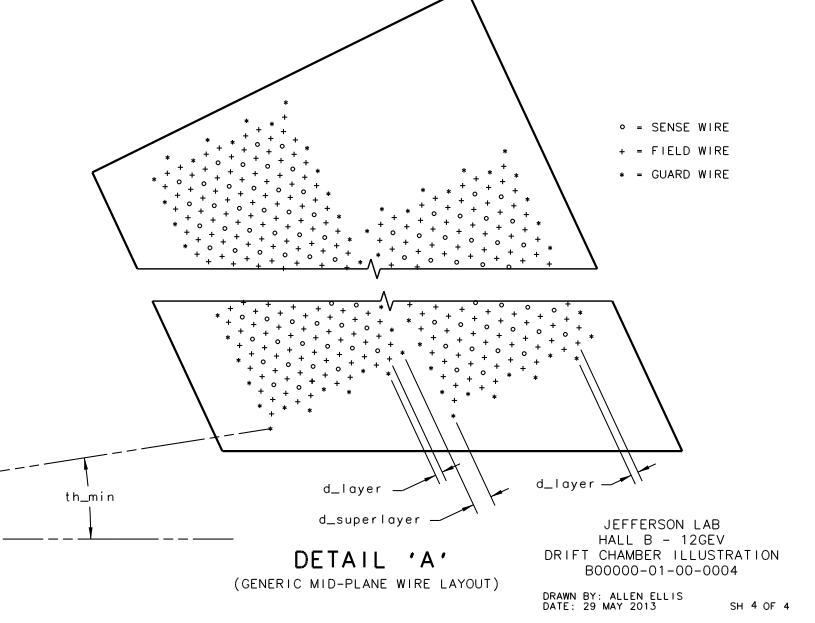
Examining the geometry file, we can see that each plane, not just the plane of the sense wires, is separated by a distance of D=.3861 cm. We can use the geometry of the wire placements to find
Finding the separation distance between two adjacent sense wires
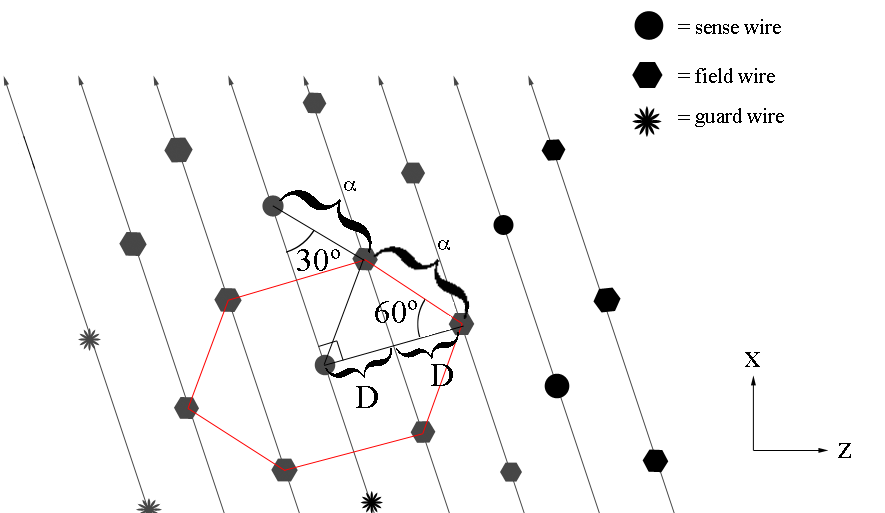
Since the separation between adjacent sense wires is uniform and at a set angle of 25 degrees with respect to the beam line, we can use this fact to determine the angle theta each wire makes when measured from the vertex.
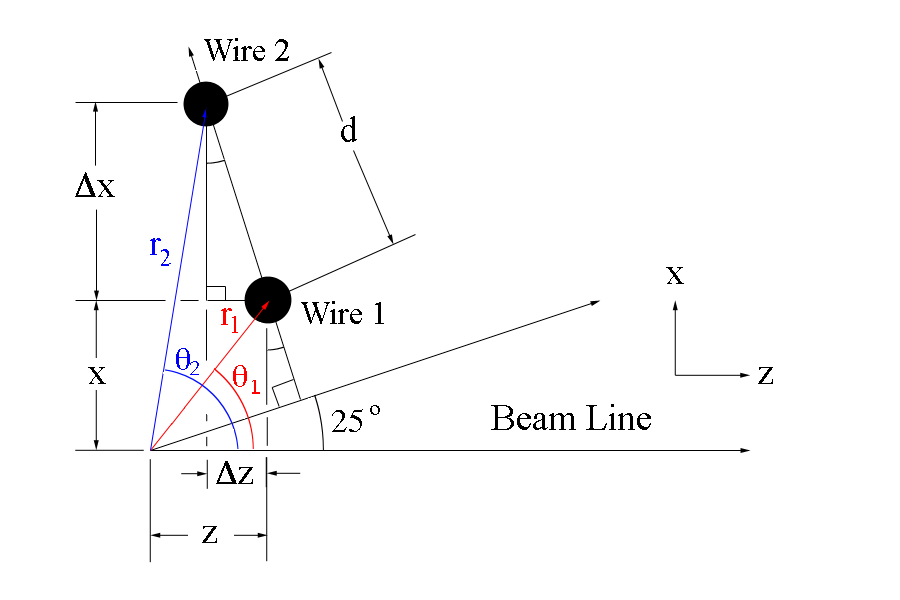
The new x and z coordinates for wire 2 can be found using the change in the components
This can be extended to any point along the same wire plane, starting from the coordinates for wire 1
The angle theta that the wire makes with the vertex is given by
CED Verification
Using CED to verify the angle and wire correlation,
Zooming in on the view paralell to the direction of the wires in ced, we can examine the wire corresponding theta angle in the drift chamber.
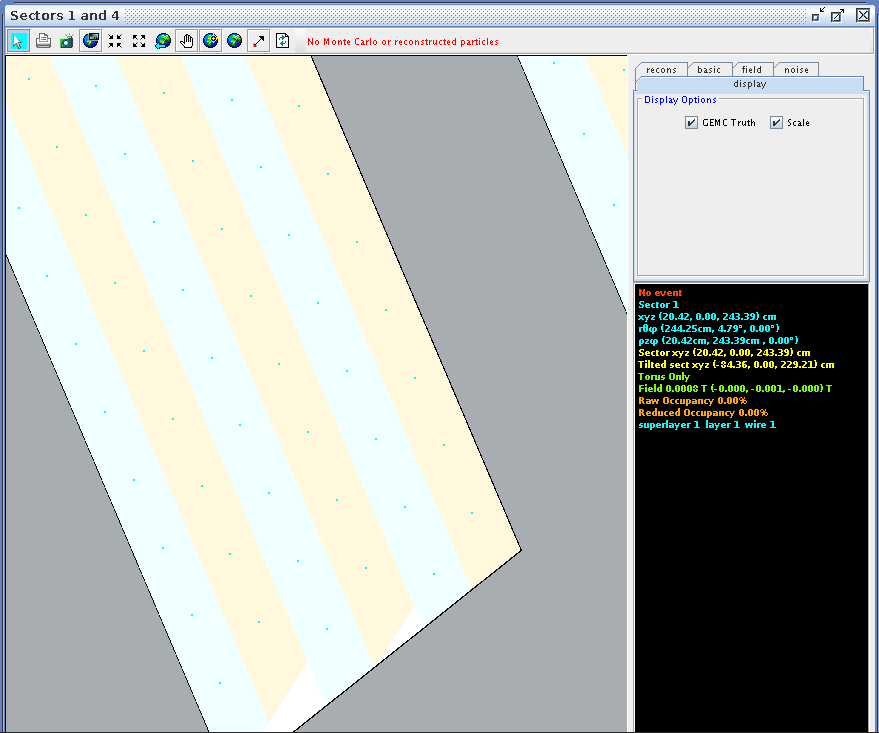
| Coordinates(cm) | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 | Layer 4 | Layer 5 | Layer 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| y | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| z | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| Coordinates(cm) | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 | Layer 4 | Layer 5 | Layer 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| y | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| z | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
Corresponding theta angles can be found for other wires, in Region 1, Superlayers 1 and 2.
| Wire Number | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 | Layer 4 | Layer 5 | Layer 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| 2 | 5.09 | 5.33 | 5.27 | 5.51 | 5.45 | 5.69 |
| 77 | 29.46 | 29.60 | 29.41 | 29.55 | 29.37 | 29.51 |
| 78 | 29.79 | 29.93 | 29.74 | 29.88 | 29.69 | 29.83 |
| 79 | 30.12 | 30.26 | 30.07 | 30.21 | 30.02 | 30.16 |
| 110 | 40.19 | 40.28 | 40.05 | 40.13 | 39.91 | 39.99 |
| 111 | 40.51 | 40.59 | 40.36 | 40.44 | 40.21 | 40.29 |
| 112 | 40.82 | 40.90 | 40.67 | 40.75 | 40.52 | 40.60 |
| Wire Number | Layer 1 | Layer 2 | Layer 3 | Layer 4 | Layer 5 | Layer 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.79 | 5.03 | 4.98 | 5.22 | 5.16 | 5.40 |
| 2 | 5.09 | 5.33 | 5.27 | 5.51 | 5.45 | 5.69 |
| 77 | 29.46 | 29.60 | 29.41 | 29.56 | 29.37 | 29.51 |
| 78 | 29.79 | 29.93 | 29.74 | 29.88 | 29.70 | 29.84 |
| 79 | 30.13 | 30.27 | 30.07 | 30.21 | 30.02 | 30.16 |
| 110x | 40.19 | 40.28 | 40.05 | 40.13 | 39.91 | 39.99 |
| 111 | 40.51 | 40.59 | 40.36 | 40.44 | 40.22 | 40.30 |
| 112 | 40.82 | 40.90 | 40.67 | 40.75 | 40.52 | 40.60 |
Super Layer 1:Layer 1
Examing the range limits for the angle theta:
Taking the difference of the upper and lower limits in theta,
Dividing by the change in wire numbers (112-1=111), we find
This would imply that if the wires were evenly placed, their change in angle theta would increase by the factor of .325 degrees for each increase in wire number, starting obviously with wire 1 at 4.79 degrees. In addition, this implies that the bin spacing for each wire would be around .325 degrees in width.
Chercking this, we can find the difference between wires 1 and 2,
Similarly, finding the difference between wires 111 and 112,
These differing values show that the bin width is not uniform in length, therefore a linear fit will not suffice.
Changing cell size
Using Mathematica, a line can be fitted to the data collected on the wire number to angle theta correspondence.
Declaring the data set:
In[1]:= data1={{1,4.79},{2,5.09},{78,29.79},{111,40.50},{112,40.82}}
Out[1]= {{1,4.79},{2,5.09},{78,29.79},{111,40.5},{112,40.82}}
Testing for a linear fit:
In[2]:= line1=Fit[data1,{1,x},x]
Out[2]= 4.45395 +0.324738 x
Since the 1st deriviative of this function is not equal to the previous value of .3246 degrees, we will need to test the next order.
Testing for a quadratic fit:
In[3]:= quad1=Fit[data1,{1,x,x^2},x]
Out[3]= 4.45253 +0.325072 x-3.05048*10^-6 x^2
Testing for a polynomial of degree 3 fit:
In[118]:= polynomial1=Fit[data1,{1,x,x^2,x^3},x]
Out[118]= 4.48739 +0.300911 x+0.000510988 x^2-2.6919*10^-6 x^3