Difference between revisions of "LB RunGroupC Vertex"
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
Two vertex variables are fixed at zero and the third vertex variable is altered. A 6 GeV electron was fired at angles of 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi. | Two vertex variables are fixed at zero and the third vertex variable is altered. A 6 GeV electron was fired at angles of 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The gcard used had the same detector parts as above, but the filename and pathways were changed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Below is a sample line from the LUND file: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1 1 1 1 1 1.00029 0.0718059 0.937771 1.48222 0.789865 | ||
| + | 1 -1 1 11 0 0 0 2.53564 5.43788 6 0.000511 0.999484 0 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Also, here are the GEMC, Coat-Java, and a sample ROOT command. | ||
| + | |||
| + | GEMC: ~/src/CLAS/GEMC/source/gemc -USE_GUI=0 -INPUT_GEN_FILE="LUND,test.LUND" -N=100 eg12.gcard | ||
| + | |||
| + | Coat-Java:~/src/CLAS/coatjava-2.4/bin/clas12-reconstruction -i ../files/vertex/vertex.evio -config GEOM::new=true -config MAG::torus=-1.0 -config MAG::solenoid=1.0 -o ../files/vertex/vertex_rec.evio -s DCHB:DCTB:EC:FTOF:EB -config DATA::mc=true -config DCTB::useRaster=true | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sample ROOT command: clas12->Draw("GenPart.x - Event.x"); | ||
{|border="5" | {|border="5" | ||
Revision as of 17:18, 26 September 2016
Vertex Reconstruction studies
Inclusive electron GEMC 2.4 & Coatjava 2.4
Summary
Set all histogram ranges to -6,6 cm and bin sizes of 0.1 cm
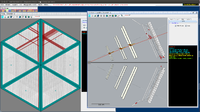
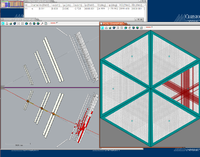
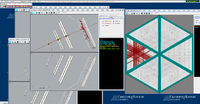
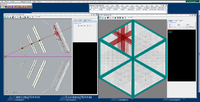
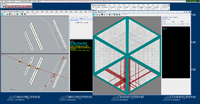
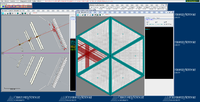
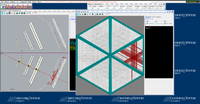
Below are some of the sample GEMC simulations as seen in the CED
Point target X,Y,Z=0 cm
The histograms below are using a 6 GeV electron fired at an angles of 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi.
For the plots below, I used the following gcard, sample LUND file, and commands in GEMC 2.4, coat-java 2.4, and ROOT
gcard:
<gcard>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/fc/forwardCarriage" factory="TEXT" variation="original"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/dc/dc" factory="TEXT" variation="ccdb"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/ec/ec" factory="TEXT" variation="original"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/ctof/ctof" factory="TEXT" variation="original"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/ftof/ftof" factory="TEXT" variation="java"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/htcc/htcc" factory="TEXT" variation="original"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/pcal/pcal" factory="TEXT" variation="javageom"/>
<detector name="../../../../clas12/magnets/solenoid" factory="TEXT" variation="original"/>
<option name="SCALE_FIELD" value="clas12-torus-big, -1"/>
<option name="HALL_FIELD" value="clas12-solenoid"/>
<option name="OUTPUT" value="evio,eg12_sol_75k_No_Raster.ev"/>
</gcard>
Sample LUND File:
1 1 1 1 1 1.00029 0.0718059 0.937771 1.48222 0.789865 1 -1 1 11 0 0 0 2.53564 5.43788 6 0.000511 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1.00029 0.0718059 0.937771 1.48222 0.789865 1 -1 1 11 0 0 0 2.53564 5.43788 6 0.000511 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1.00029 0.0718059 0.937771 1.48222 0.789865 1 -1 1 11 0 0 0 2.53564 5.43788 6 0.000511 0 0 0
GEMC Command:
~/src/CLAS/GEMC/source/gemc -USE_GUI=0 -INPUT_GEN_FILE="LUND,No_Raster.LUND" -N=75000 eg12_sol_No_Raster.gcard
Coat-Java 2.4 command:
~/src/CLAS/coatjava-2.4/bin/clas12-reconstruction -i ../files/vertex/vertex.evio -config GEOM::new=true -config MAG::torus=-1.0 -config MAG::solenoid=1.0 -o ../files/vertex/vertex_rec.evio -s DCHB:DCTB:EC:FTOF:EB -config DATA::mc=true -config DCTB::useRaster=true
Sample ROOT command:
clas12->Draw("GenPart.x - Event.x","abs(Event.x)<3");
| No Rastering | |
|---|---|
| Vx Difference | 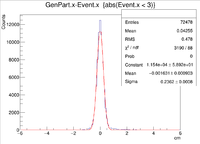
|
| Vy Difference | 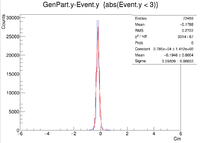
|
| Vz Difference | 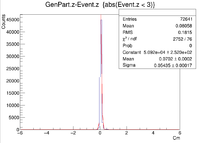
|
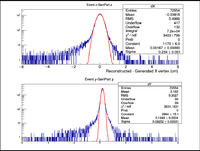
| X Resolution (cm) | 0.2362 +/- 0.0008 |
| Y Resolution(cm) | 0.09809 +/- 0.00033 |
| Z Resolution (cm) | 0.05435 +/- 0.00017 |
These histograms raise some questions. To begin I created a LUND file with 6 GeV incident electrons at 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi. All of the vertex positions were set to 0. I then ran GEMC 2.4 using the command line ~/src/CLAS/GEMC/source/gemc -USE_GUI=0 -INPUT_GEN_FILE="LUND,No_Raster.LUND" -N=75000 eg12_sol_No_Raster.gcard
which created an output file called eg12_sol_75k_No_Raster.ev. After that the reconstruction command line used was
~/src/CLAS/coatjava-2.4/bin/clas12-reconstruction -i eg12_sol_75k_No_Raster.ev-config GEOM::new=true -config MAG::torus=-1.0 -config MAG::solenoid=1.0 -o eg12_sol_75k_No_Raster_rec.evio -s DCHB:DCTB:EC:FTOF:EB -config DATA::mc=true -config DCTB::useRaster=true
After the reconstruction a root file was created using
~/src/CLAS/evio2root/bin/evio2root eg12_sol_75k_No_Raster_rec.evio eg12_sol_75k_No_Raster_rec.root 75000
A plot was then created to show the X Vertex and Y Vertex Differences
The first question is why is there a shift in the Y Difference. What would make X more centered around 0? The next question is when rastering begins, why do the resolutions in the X Vertices remain unchanged while the resolutions in the Y Vertices change?
Point in 2-D but extended target in 1-D
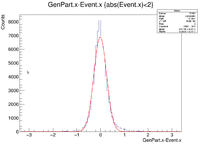
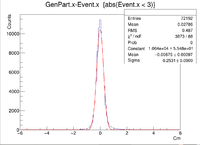
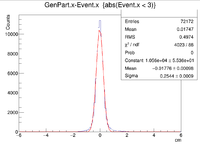
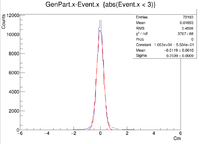
Two vertex variables are fixed at zero and the third vertex variable is altered. A 6 GeV electron was fired at angles of 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi.
The gcard used had the same detector parts as above, but the filename and pathways were changed.
Below is a sample line from the LUND file:
1 1 1 1 1 1.00029 0.0718059 0.937771 1.48222 0.789865 1 -1 1 11 0 0 0 2.53564 5.43788 6 0.000511 0.999484 0 0
Also, here are the GEMC, Coat-Java, and a sample ROOT command.
GEMC: ~/src/CLAS/GEMC/source/gemc -USE_GUI=0 -INPUT_GEN_FILE="LUND,test.LUND" -N=100 eg12.gcard
Coat-Java:~/src/CLAS/coatjava-2.4/bin/clas12-reconstruction -i ../files/vertex/vertex.evio -config GEOM::new=true -config MAG::torus=-1.0 -config MAG::solenoid=1.0 -o ../files/vertex/vertex_rec.evio -s DCHB:DCTB:EC:FTOF:EB -config DATA::mc=true -config DCTB::useRaster=true
Sample ROOT command: clas12->Draw("GenPart.x - Event.x");
Extended target -3 < Z < 3 cm
VertREC_9-22-16_table_3ltZgt-3
Extended target in Z. Vy shift analysis
All Histograms below were created by simply making the target longer along the Z axis. Each case uses vertex points for X and Y ranging from -1cm to 1cm
VertREC_9-22-16_table_3ltZgt-3_1gtRlt-1
Localized Vertex Resolution Investigation of Line Targets
GEMC was ran to create electrons being produced in a line along certain axes. These include three separate 2cm targets centered at (0,0,0) in the X, Y , and Z directions. The final target is a line along the Z axis centered at (0,0,0) that is 6cm long. The generated electrons were shot at 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi at an energy of 6GeV.
Here is an example of how the cuts were made. Consider the case of a 2cm line target in the Z direction centered at (0,0,0). Closed intervals begin at the end of the target and are 0.1cm long. So the first interval would be [-1.0,-0.9], then the next would be [-0.9, -0.8] and so on until the entire target is covered. The events in the EVENTHB bank were cut so that in any given interval there would be a margin of +/- 1cm to remove any outliers that may cause the histograms to have long tails.
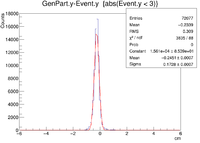
Below are the histograms for the 2cm line target in Y,X=0,Z=0. The electrons were fired with an energy of 6 GeV at 25 degrees in theta at 0 degrees in phi.
2cm YLineTarg 0 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
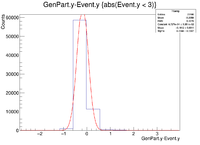
Below are the histograms for a 2cm target along the Y axis, X = 0 Z = 0. The electrons were fired with an energy of 6 GeV at 25 degrees in theta and 180 degrees in phi.
2cm YLineTarg 180 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
Below are the Histograms for a 2cm long target in the X Direction with a 6GeV electron fired at 25 degrees in theta and 90 degrees in phi
2cm XLineTarg 90 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
Below are the Vx Differences using a 2cm target in X with incident 6 GeV electrons at 25 degrees in theta and 270 degrees in phi
2cm XLineTarg 270 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
Below are the histograms for a 6cm target in the Z direction using a 6 GeV electron fired at 25 degrees in theta and 0 degrees in phi.
6cm ZLineTarg 0 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
Below are the histograms for a 6cm target in the Z direction using a 6 GeV electron fired at 25 degrees in theta and 90 degrees in phi.
6cm ZLineTarg 90 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
Below are the histograms for a 6 GeV electron fired at angles 25 degrees in theta and 270 degrees in phi. The target was 6cm in the Z direction.
6cm ZLineTarg 270 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
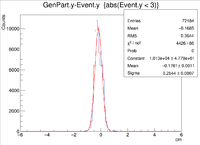
Below are the histograms for a 2cm target along the Y axis, X = 0 Z = 0. The electrons were fired with an energy of 6 GeV at 25 degrees in theta and 30 degrees in phi.
2cm YLineTarg 30 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
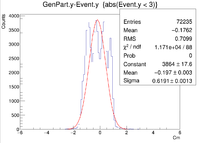
Below are the histograms for a 2cm Y target with an incident electron energy of 6 GeV. The angles were theta = 25 degrees and phi = 210 degrees
2cm YLineTarg 210 Degree Rotation 09/23/16
Localized Vertex Resolution Investigation of 2 Dimensional Targets
The histograms below were created using a 6 GeV electron fired at 25 degrees in theta and 30 degrees in phi. To make the cuts I simply made circles of increasing radius centered at the origin. I used 0.1cm increments to make the 10 histograms for each vertex position.
Below are the Vx and Vy Differences for a 2cm XY target, Z=0.
2cm XYTarg Z=0 Vx and Vy Differences 09/23/16
Below are the Vy and Vz differences for a 2cm target in Y and Z, X=0. The electrons were fired with an energy of 6 GeV and angles of 25 degrees in theta and 30 degrees in phi.
2cm YZTarg X=0 Vz and Vy Difference 09/23/16
Below are the Vx and Vz differences for a 2cm XZ target, Y = 0. The electrons were fired with an energy of 6 GeV at angles theta = 25 degrees and phi = 30 degrees.
2cm XZTarg Y=0 Vx and Vz Differences 09/23/16
Localized Vertex Resolution of 3 Dimensional targets
For the plots below, a 6 GeV electron was fired at angles 25 degrees in theta and 30 degrees in phi. The target has an XY radius of 1cm and a length in the Z direction of 6cm. Setting GenPart.z = 0cm, the resolution was investigated as a function of the target's XY radius along with a table for the values.
In this section, concentric rings with a thickness of 0.1cm were created within the target. For example these plots would include a ring centered at x=y=z=0 and include all GenPart.x and GenPart.y from (0.0 cm, 0.1 cm), then another ring would include all Genpart.x and GenPart.y events from (0.1 cm, 0.2 cm) and so on until we reach the edge of the target.
clas12->Draw("Event.z >> (100,-5,5)","sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)<0.95 && sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)>0.85");
| R (cm) | 0.05 +/- 0.05 | 0.15 +/- 0.05 | 0.25 +/- 0.05 | 0.35 +/- 0.05 | 0.45 +/- 0.05 | 0.55 +/- 0.05 | 0.65 +/- 0.05 | 0.75 +/- 0.05 | 0.85 +/- 0.05 | 0.95 +/- 0.05 |
| Width (cm) | 0.05094 +/- 0.0019 | 0.07812 +/- 0.0018 | 0.3688 +/- 0.0063 | 0.5231 +/- 0.0077 | 0.718 +/- 0.012 | 0.7987 +/- 0.0092 | 0.8709 +/- 0.0085 | 1.038 +/- 0.01 | 1.183 +/- 0.012 | 1.296 +/- 0.013 |
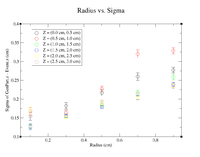
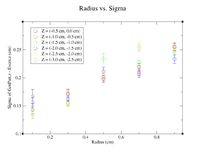
For the next set of plots, the GEMC simulations had the same energy and angles as above. To construct scatter plots, similar annular cuts in the radius were made (similar to above), but this time the thickness of each ring was 0.2 cm (to ensure enough events were present). In addition, the target will become extended in Z. Cuts were made in Z by restricting GenPart.z to be within a range of certain values. Each "washer" shape has a thickness of 0.5 cm in the Z direction. Histograms were created using the following command line as an example
clas12->Draw("GenPart.z - Event.z >> (100,-5,5)","sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)<0.2 && sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)>0.0 && GenPart.z > 0.0 && GenPart.z < 0.5");
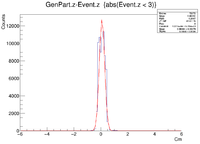
Below is a plot and a table for the Radius vs. Sigma of GenPart.z - Event.z for several cuts in Z. For the plot each Radius is centered at the point plotted with a width of +/- 0.1 cm.
| Z = (0.0 cm, 0.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1548 +/- 0.0106 | 0.1825 +/- 0.0086 | 0.2167 +/- 0.0078 | 0.26 +/- 0.01 | 0.2774 +/- 0.0075 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (0.5 cm, 1.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1672 +/- 0.0109 | 0.1636 +/- 0.0064 | 0.2277 +/- 0.0075 | 0.3203 +/- 0.0107 | 0.3287 +/- 0.0082 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (1.0 cm, 1.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1282 +/- 0.0068 | 0.1551 +/- 0.0042 | 0.1842 +/- 0.0052 | 0.2172 +/- 0.0069 | 0.2587 +/- 0.0072 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (1.5 cm, 2.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1264 +/- 0.0071 | 0.1558 +/- 0.0042 | 0.1795 +/- 0.0043 | 0.2034 +/- 0.0049 | 0.2391 +/- 0.0055 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (2.0 cm, 2.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1723 +/- 0.0120 | 0.1519 +/- 0.0038 | 0.1896 +/- 0.0048 | 0.2033 +/- 0.0043 | 0.2361 +/- 0.0048 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (2.5 cm, 3.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1273 +/- 0.0054 | 0.1665 +/- 0.0057 | 0.1936 +/- 0.0041 | 0.2143 +/- 0.0042 | 0.2337 +/- 0.0050 |
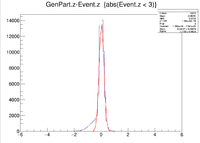
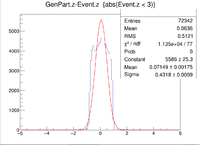
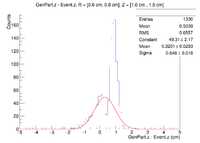
Here is where the problem of a bimodal distribution become relevant as seen below in the histogram.
For now I will simply fit the larger peak to hopefully get rid of the muddling of the resolution, but this must be noted and investigated further later.
Below is the plot and the table for the negative half of the target.
| Z = (-0.5 cm, 0.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1666 +/- 0.0128 | 0.1722 +/- 0.0078 | 0.1983 +/- 0.0067 | 0.2193 +/- 0.0060 | 0.2554 +/- 0.0068 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (-1.0 cm, -0.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1435 +/- 0.0069 | 0.1708 +/- 0.0068 | 0.2008 +/- 0.0069 | 0.2094 +/- 0.0058 | 0.2544 +/- 0.0065 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (-1.5 cm, -1.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1418 +/- 0.0073 | 0.1551 +/- 0.0047 | 0.2342 +/- 0.0092 | 0.2286 +/- 0.0066 | 0.2459 +/- 0.0066 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (-2.0 cm, -1.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1562 +/- 0.0091 | 0.1628 +/- 0.0045 | 0.2115 +/- 0.0076 | 0.2061 +/- 0.0056 | 0.2335 +/- 0.0077 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (-2.5 cm, -2.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1312 +/- 0.0059 | 0.1517 +/- 0.0040 | 0.2061 +/- 0.0049 | 0.257 +/- 0.008 | 0.2484 +/- 0.005 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (-3.0 cm, -2.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1339 +/- 0.0065 | 0.1539 +/- 0.0038 | 0.202 +/- 0.004 | 0.2537 +/- 0.0061 | 0.2517 +/- 0.0062 |
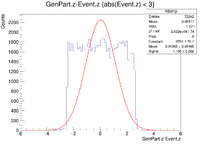
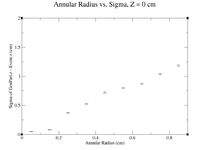
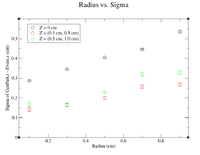
It would seem that the bimodal distribution is having an effect on the results. It is counterintuitive that the resolution would get better the farther away from zero the events are. To begin investigating this, I made a Radius vs. Sigma plot for several values of Z. Here are some sample command lines in ROOT to get the width of the Gaussian peak.
clas12->Draw("Event.z >> (100,-5,5)","sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)<1.0 && sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)>0.8 && GenPart.z = 0");
clas12->Draw("GenPart.z - Event.z >> (100,-5,5)","sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)<0.6 && sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)>0.4 && GenPart.z > 0.1 && GenPart.z < 0.5");
clas12->Draw("GenPart.z - Event.z >> (100,-5,5)","sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)<0.6 && sqrt(GenPart.x*GenPart.x+GenPart.y*GenPart.y)>0.4 && GenPart.z > 0.5 && GenPart.z < 1.0");
| Z = 0.0 cm | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.2873 +/- 0.0035 | 0.3457 +/- 0.0026 | 0.4045 +/- 0.0026 | 0.4466 +/- 0.0026 | 0.5359 +/- 0.0033 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (0.1 cm, 0.5 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.141 +/- 0.010 | 0.1651 +/- 0.0086 | 0.1991 +/- 0.0082 | 0.2572 +/- 0.0093 | 0.2676 +/- 0.0081 |
| ******************************************* | |||||
| Z = (0.5 cm, 1.0 cm) | |||||
| R (cm) | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| Sigma (cm) | 0.1672 +/- 0.0109 | 0.1636 +/- 0.0064 | 0.2277 +/- 0.0075 | 0.3203 +/- 0.0107 | 0.3287 +/- 0.0082 |
Elastic electron proton GEMC 2.4 & Coatjava 2.4
References
https://clasweb.jlab.org/wiki/index.php/TF_EG12_Vertex#Z_resolution_With_micro-megas