Difference between revisions of "Variables Used in Elastic Scattering"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
where represents the 4-Momentum Vector in the CM frame
and represents the 4-Momentum Vector in the initial Lab frame
where represents the 4-Momentum Vector in the final Lab frame
and represents the 4-Momentum Vector in the final CM frame
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
and the fact that the length of these 4-Momentum Vectors are invariant, | and the fact that the length of these 4-Momentum Vectors are invariant, | ||
| − | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_1}- {\mathbf P_1^'}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_1}^2-2{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P_1^'}+ {\mathbf P_1^'}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_1-E_1'\\ p_{1(x)}-p_{1(x)}^' \\ p_{1(y)}-p_{1(y)}^' \\ p_{1(z)}-p_{1(z)}^'\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_a}\right)^2=s</math></center> | + | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_1^*}- {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_1^*}^2-2{\mathbf P_1^*}\cdot {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}+ {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_1^*-E_1^{'*}\\ p_{1(x)}^*-p_{1(x)}^{'*} \\ p_{1(y)}^*-p_{1(y)}^{'*} \\ p_{1(z)}^*-p_{1(z)}^{'*}\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_a^*}\right)^2=s</math></center> |
| − | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_1}- {\mathbf P_2^'}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_1}^2-2{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P_2^'}+ {\mathbf P_2^'}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_1-E_2'\\ p_{1(x)}-p_{2(x)}^' \\ p_{1(y)}-p_{2(y)}^' \\ p_{1(z)}-p_{2(z)}^'\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_b}\right)^2=s</math></center> | + | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_1^*}- {\mathbf P_2^{'*}}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_1^*}^2-2{\mathbf P_1^*}\cdot {\mathbf P_2^{'*}}+ {\mathbf P_2^{'*}}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_1^*-E_2^{'*}\\ p_{1(x)}^*-p_{2(x)}^{'*} \\ p_{1(y)}^*-p_{2(y)}^{'*} \\ p_{1(z)}^*-p_{2(z)}^{'*}\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_b^*}\right)^2=s</math></center> |
| − | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_2}- {\mathbf P_1^'}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_2}^2-2{\mathbf P_2}\cdot {\mathbf P_1^'}+ {\mathbf P_1^'}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_2-E_1'\\ p_{2(x)}-p_{1(x)}^' \\ p_{2(y)}-p_{1(y)}^' \\ p_{2(z)}-p_{1(z)}^'\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_c}\right)^2=s</math></center> | + | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_2^*}- {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_2^*}^2-2{\mathbf P_2^*}\cdot {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}+ {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_2^*-E_1^{'*}\\ p_{2(x)}^*-p_{1(x)}^{'*} \\ p_{2(y)}^*-p_{1(y)}^{'*} \\ p_{2(z)}^*-p_{1(z)}^{'*}\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_c^*}\right)^2=s</math></center> |
| − | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_2}- {\mathbf P_2^'}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_2}^2-2{\mathbf P_2}\cdot {\mathbf P_2^'}+ {\mathbf P_2^'}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_2-E_2'\\ p_{2(x)}-p_{2(x)}^' \\ p_{2(y)}-p_{2(y)}^' \\ p_{2(z)}-p_{2(z)}^'\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_d}\right)^2=s</math></center> | + | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_2^*}- {\mathbf P_2^{'*}}\right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_2^*}^2-2{\mathbf P_2^*}\cdot {\mathbf P_2^{'*}}+ {\mathbf P_2^{'*}}\right)= \left( \begin{matrix}E_2^*-E_2^{'*}\\ p_{2(x)}^*-p_{2(x)}^{'*} \\ p_{2(y)}^*-p_{2(y)}^{'*} \\ p_{2(z)}^*-p_{2(z)}^{'*}\end{matrix} \right)^2=\left({\mathbf P_d^*}\right)^2=s</math></center> |
Using the fact that the scalar product of a 4-momenta with itself is invariant, | Using the fact that the scalar product of a 4-momenta with itself is invariant, | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
| − | <center><math>{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P^1}=E_1E_1-\vec p_1\cdot \vec p_1 =m_{1}^2 | + | <center><math>{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P^1}=E_1E_1-\vec p_1\cdot \vec p_1 =m_{1}^2</math></center> |
We can simiplify the expressions | We can simiplify the expressions | ||
| − | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_1}- {\mathbf P_1^'}\right)^2=\left( m_1^2-2{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P_1^'}+ m_1^{'2}\right)=\left({\mathbf P_a}\right)^2=s</math></center> | + | <center><math>\left({\mathbf P_1^*}- {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}\right)^2=\left( m_1^{*2}-2{\mathbf P_1^*}\cdot {\mathbf P_1^{'*}}+ m_1^{'*2}\right)=\left({\mathbf P_a^*}\right)^2=s</math></center> |
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
<center><math>{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P^'}=\left(\begin{matrix} E\\ p_x \\ p_y \\ p_z \end{matrix} \right)\cdot \left( \begin{matrix}1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\0 &0 & 0 &-1\end{matrix} \right)\cdot \left(\begin{matrix} E' & p_x^' & p_y^' & p_z^' \end{matrix} \right)=E_1E_1^'-\vec p_1\cdot \vec p_1^' </math></center> | <center><math>{\mathbf P_1}\cdot {\mathbf P^'}=\left(\begin{matrix} E\\ p_x \\ p_y \\ p_z \end{matrix} \right)\cdot \left( \begin{matrix}1 & 0 & 0 & 0\\0 & -1 & 0 & 0\\0 & 0 & -1 & 0\\0 &0 & 0 &-1\end{matrix} \right)\cdot \left(\begin{matrix} E' & p_x^' & p_y^' & p_z^' \end{matrix} \right)=E_1E_1^'-\vec p_1\cdot \vec p_1^' </math></center> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
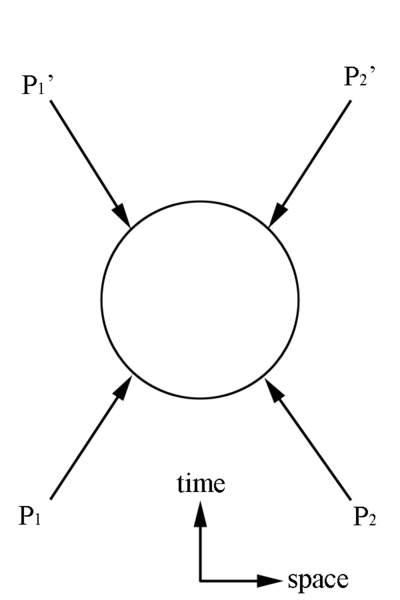
=Mandelstam Representation= | =Mandelstam Representation= | ||
[[File:Mandelstam.png | 400 px]] | [[File:Mandelstam.png | 400 px]] | ||
Revision as of 23:35, 31 January 2016
Lorentz Invariant Quantities
Total 4-Momentums
As was shown earlier the scalar product of a 4-Momentum vector with itself ,
,
and the length of a 4-Momentum vector composed of 4-Momentum vectors,
,
are invariant quantities.
It was further shown that
which can be expanded to
New 4-Momentum Quantities
Working in just the CM frame, we can form new 4-Momentum Vectors comprised of 4-Momenta in this frame, with
Using the algebraic fact
and the fact that the length of these 4-Momentum Vectors are invariant,
Using the fact that the scalar product of a 4-momenta with itself is invariant,
We can simiplify the expressions
Finding the cross terms,