Difference between revisions of "Forest PHYS100 Chapt2"
| (30 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Average speed== | ==Average speed== | ||
| − | Average speed is the ratio of | + | Average speed <math>(s)</math> is the ratio of the DISTANCE <math>(d)</math> you have traveled divided by the time <math>(t)</math> it took you to travel that distance. |
| + | :<math>\mbox{Average Speed} = \frac{\mbox{Distance traveled}}{\mbox{Time traveled}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can write a formula to express the definition of speed using the above abreviations for speed, distance, and time | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\bar s = \frac{d}{t}</math> | ||
| + | The bar over the <math>s</math> just used to indicate that it is an average. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==An example of calculating your average speed== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suppose you drive from Pocatello to a friends house in Salt Lake. You know that the distance is 150 miles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If it takes you 3 hours to drive there then your average speed is | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\bar s = \frac{150 \mbox{miles}}{3 \mbox{hours}}= 50 \frac{ \mbox{miles}}{ \mbox{hours}} = 50 \mbox{ MPH}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | International System's (SI) unit for speed is | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\frac{ \mbox{meters}}{ \mbox{sec}} =\frac{ \mbox{m}}{ \mbox{s}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Unit conversion=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Converting the units from MPH to m/s is a matter of multiplying by '''1'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here are some useful expressions for 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | : <math>1 = \frac{ 1609 \mbox{ m}}{ \mbox{miles}}=\frac{ 1 \mbox{hour}}{ 60 \mbox{minutes}}=\frac{ 1 \mbox{minute}}{ 60 \mbox{seconds}}=\frac{ 1 \mbox{hours}}{ 3600 \mbox{seconds}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;We can now convert MPH to m/s by multiplying by 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\bar s = 50 \frac{ \mbox{ miles}}{ \mbox{hours}} \left ( \frac{ 1609 \mbox{m}}{ \mbox{miles}}\right )\left (\frac{ 1 \mbox{hours}}{ 3600 \mbox{seconds}}\right ) = 22 \frac{ \mbox{m}}{ \mbox{s}} </math> | ||
==Instantaneous speed== | ==Instantaneous speed== | ||
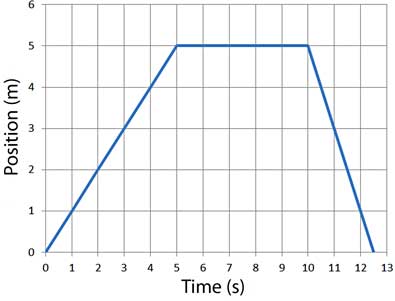
| − | + | The instantaneous speed at a given instant in time. You can see the instantaneous speed on your drive to Salt Lake City every time you look at your speedometer. | |
| + | |||
| + | Instantaneous speed can tell you how long it will take to get to Salt Lake City if the speed is constant and doesn't change. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Unfortunately, Malad pass slows my car down. A more realistic way to predict my driving time to Salt Lake City is to use the average speed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Forest_PHYS100_Ch2_dist-vs-time.jpg | 400 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
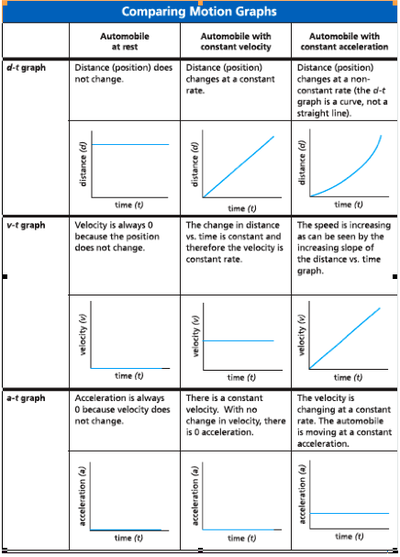
| + | [[File:Forest_PHYS100_Ch2_motion-vs-time.jpg | 400 px]] | ||
==Velocity== | ==Velocity== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:44, 30 August 2014
Chapt 2 Motion
Newton's Principia published in 1687 ( in latin and then 1726 in english).
Average speed
Average speed is the ratio of the DISTANCE you have traveled divided by the time it took you to travel that distance.
We can write a formula to express the definition of speed using the above abreviations for speed, distance, and time
The bar over the just used to indicate that it is an average.
An example of calculating your average speed
Suppose you drive from Pocatello to a friends house in Salt Lake. You know that the distance is 150 miles.
If it takes you 3 hours to drive there then your average speed is
International System's (SI) unit for speed is
Unit conversion
Converting the units from MPH to m/s is a matter of multiplying by 1.
Here are some useful expressions for 1
- We can now convert MPH to m/s by multiplying by 1
Instantaneous speed
The instantaneous speed at a given instant in time. You can see the instantaneous speed on your drive to Salt Lake City every time you look at your speedometer.
Instantaneous speed can tell you how long it will take to get to Salt Lake City if the speed is constant and doesn't change.
Unfortunately, Malad pass slows my car down. A more realistic way to predict my driving time to Salt Lake City is to use the average speed.