Difference between revisions of "B-field calculation"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (37 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:B_field_trajectory2.jpg |300px]] |
| + | <math>1 MeV = 1.6\cdot 10^{-13} J = 1.6\cdot 10^{-13} \frac{m^2\cdot kg}{s^2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>c = 2.998 \cdot 10^8 \frac{m}{s}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{MeV}{C} = 0.534 \cdot 10^{-21} \frac{m\cdot kg}{s}</math> | ||
<math>p_e = 14 \frac{MeV}{c} = 7.47 \cdot 10^{-21} \frac{m\cdot kg}{s}</math> | <math>p_e = 14 \frac{MeV}{c} = 7.47 \cdot 10^{-21} \frac{m\cdot kg}{s}</math> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 13: | ||
<math>B = \frac{p_e}{q_e \cdot R}</math> | <math>B = \frac{p_e}{q_e \cdot R}</math> | ||
| − | <math>1T=\frac{kg}{C\cdot s}</math>, <math>q_e = 1.6\cdot 10^{-19} C</math> | + | <math>1T=\frac{kg}{C\cdot s}</math>, <math>q_e = 1.6\cdot 10^{-19} C</math>, <math>1T=10^{-4}G</math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>B(T) = \frac{p_e (\frac{MeV}{c})\cdot 0.33\cdot 10^{-2}}{R(m)}</math> | ||
| + | |||
<math>B(T) = \frac{4.67\cdot 10^{-2}}{R(m)}</math> | <math>B(T) = \frac{4.67\cdot 10^{-2}}{R(m)}</math> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 26: | ||
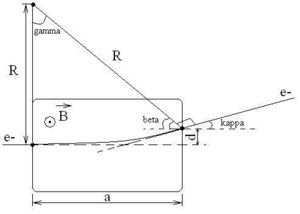
<math>\kappa = \gamma</math> | <math>\kappa = \gamma</math> | ||
| − | <math>d = R (1 - cos(\kappa))</math> | + | <math>R = \frac{a}{cos(\beta)} = \frac{a}{cos(90^0 - \kappa)} = \frac{a}{sin(\kappa)}</math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>d = R \cdot (1 - cos(\kappa)) = \frac{a \cdot (1 - cos(\kappa))}{sin(\kappa)}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B(T) = \frac{p_e (\frac{MeV}{c})\cdot 0.33\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot sin(\kappa)}{a(m)}</math> - general expression for B-field. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B(T) = \frac{4.67\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot sin(\kappa)}{a(m)}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If <math>\kappa = 2^0</math> then <math>sin(\kappa) = 0.0348995</math> and our B-field becomes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B(T) = \frac{0.163\cdot 10^{-2}}{a(m)}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a \simeq 0.12 m</math> for the coils under consideration. Hence, B-field is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B = 0.01358 T = 135.8 G</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://wiki.iac.isu.edu/index.php/PhotoFission_with_Polarized_Photons_from_HRRL Go Back] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:17, 5 February 2009
, ,
- general expression for B-field.
If then and our B-field becomes:
for the coils under consideration. Hence, B-field is: