Difference between revisions of "Lab 23 TF EIM"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
==Capacitor in parallel with <math>R_2</math>== | ==Capacitor in parallel with <math>R_2</math>== | ||
| + | [[File:TF_EIM_Lab23_c.png | 200 px]] | ||
#Select a capacitor such that<math> \frac{1}{\omega C_2} \approx R_2</math> when <math>\omega</math>= 10 kHz. | #Select a capacitor such that<math> \frac{1}{\omega C_2} \approx R_2</math> when <math>\omega</math>= 10 kHz. | ||
| − | #Add the capacitor in parallel to <math>R_2</math> so you have the circuit shown | + | #Add the capacitor in parallel to <math>R_2</math> so you have the circuit shown above. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#Use a pulse generator to input a sinusoidal voltage <math>V_{in}</math> | #Use a pulse generator to input a sinusoidal voltage <math>V_{in}</math> | ||
# Measure the Gain as a function of the <math>V_{in}</math> frequency and plot it. | # Measure the Gain as a function of the <math>V_{in}</math> frequency and plot it. | ||
Revision as of 23:39, 9 April 2011
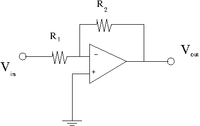
Inverting OP Amp
1. Construct the inverting amplifier according to the wiring diagram below.
2. insert a 0.1 F capacitor between ground and the OP power supply input pin.
Gain measurements
- Measure the gain as a function of frequency between 100 Hz and 2 MHz for three values of R_2 = 10 k, 100 k, 1M.
- Graph the above measurements with the Gain in units of decibels (dB) and with a logarithmic scale for the frequency axis.
Impedance
Input Impedance
- Measure for the 10 fold and 100 fold amplifier at ~100 Hz and 10 kHz frequency.
Output Impedance
- Measure for the 10 fold and 100 fold amplifier at ~100 Hz and 10 kHz frequency. Be sure to keep the output () undistorted
and
Use the above equation and two measurements of , , and to extract and .
- measure for = 1 k, = 100 k, and=0 (grounded).
- measure for = 10 k, = 1 M, and=0 (grounded).
- You can now construct 2 equations with 2 unknowns and .
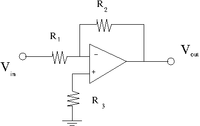
Now we will put in a pull up resistor R_3 as shown below.
Instead of the current we have the current
Use the same technique and resistors from the previous section to construct 2 equations and 2 unknowns and extract , keep =0.
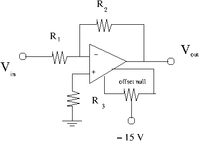
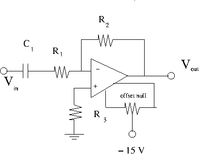
The offset Null Circuit
- Construct the offset null circuit above.
- Adjust the potentiometer to minimize with .
- Use a scope to measure the output noise.
Capacitors
- Revert back to the pull up resistor
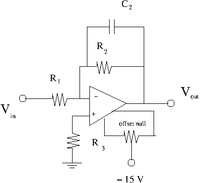
Capacitor in parallel with
- Select a capacitor such that when = 10 kHz.
- Add the capacitor in parallel to so you have the circuit shown above.
- Use a pulse generator to input a sinusoidal voltage
- Measure the Gain as a function of the frequency and plot it.
Capacitor in series with R_1
- Select a capacitor such that when = 1 kHz.
- Add the capacitor in series to so you have the circuit shown below.
- Use a pulse generator to input a sinusoidal voltage
- Measure the Gain as a function of the frequency and plot it.
Slew rate
Measure the slew and compare it to the factory spec.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
- Set V_{in} = 0.
- Measure while changing