Difference between revisions of "Lab 14 RS"
| (162 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<math>I_C = \frac{V_{CC}-V_{CE}}{R_E+R_C} = \frac{(11 - V_{CE})\ V}{2.2\ k\Omega} </math> | <math>I_C = \frac{V_{CC}-V_{CE}}{R_E+R_C} = \frac{(11 - V_{CE})\ V}{2.2\ k\Omega} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | About <math>R_1</math>, <math>R_2</math> and <math>R_E</math>, <math>C_1</math>, <math>C_2</math> and <math>C_E</math> see my calculations below. | ||
==Draw a load line using the <math>I_{C}</math> -vs- <math>I_{EC}</math> from the previous lab 13. Record the value of <math>h_{FE}</math> or <math>\beta</math>.== | ==Draw a load line using the <math>I_{C}</math> -vs- <math>I_{EC}</math> from the previous lab 13. Record the value of <math>h_{FE}</math> or <math>\beta</math>.== | ||
| Line 45: | Line 48: | ||
<math>\beta \approx 170</math> | <math>\beta \approx 170</math> | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==Set a DC operating point <math>I^{\prime}_C</math> so it will amplify the input pulse given to you. Some of you will have sinusoidal pulses others will have positive or negative only pulses.== | ==Set a DC operating point <math>I^{\prime}_C</math> so it will amplify the input pulse given to you. Some of you will have sinusoidal pulses others will have positive or negative only pulses.== | ||
| Line 62: | Line 66: | ||
<math>V_E = I_E \cdot R_E = 2.5\ mA \cdot 0.2\ k\Omega = 0.5\ V</math> | <math>V_E = I_E \cdot R_E = 2.5\ mA \cdot 0.2\ k\Omega = 0.5\ V</math> | ||
| − | <math>V_B = V_E + | + | <math>V_B = V_E + V_{BE} = (0.50 + 0.68)\ V = 1.18\ V</math> |
| Line 72: | Line 76: | ||
| − | To get operating point independent of the transistor base current we want <math>I_{R1} \gg\ I_B</math> | + | To get operating point independent of the transistor base current we want <math>I_D = I_{R1} \gg\ I_B</math> |
Let's <math>I_{R1} = 590\ uA \gg\ I_B = 14.4\ uA</math> | Let's <math>I_{R1} = 590\ uA \gg\ I_B = 14.4\ uA</math> | ||
| Line 97: | Line 101: | ||
| + | Now when we know all resistor values we are ready to calculate capacitor values. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1) To prevent decreasing in gain we need to make capacitance <math>C_E</math> large enough so the <math>X_C</math> will become small enough compared to <math>R_E</math> to make AC signal grounded. Also note that the DC bias is not affected because <math>C_E</math> will not pass the direct current. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>X_C = \frac{1}{\omega C_E} \ll R_E</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | So | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>C_E \gg \frac{1}{\omega_{min}R_E} = \frac{1}{(2\pi)(20\ Hz)(200\ \Omega)} = 40 \mu F</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | I choose the electrolytic capacitor: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>C_E = 100\ \mu F</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 2) Now we need to block the amplifier from input and output signal to avoid change the DC bias. We can do it by placing the "blocking" capacitor, in series in-front and in-back of the amplifier. They both form the high-pass filter. And if we want to amplify the frequency more than <math>20\ Hz</math> we need to choose the breakpoint frequency to be: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\omega_B = \frac{1}{RC} \ll (2\pi\ 20)\ Hz</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | For the output high-pass filter from the ac equivalent circuit we have <math>R = R_L</math> where the resistance <math>R_L</math> is the resistance of the output device. Let's <math>R_L = 10\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | So | ||
| + | <math>C_2 \gg \frac{1}{(2\pi\ 20)\ R_L} = \frac{1}{(2\pi\ 20)\ 10\ k\Omega} = 0.8\times10^{-6} F</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | For the input high-pass filter from the ac equivalent circuit we have | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{1}{R} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \frac{1}{R_{BE}} = \frac{1}{2\ k\Omega} + \frac{1}{16.25\ k\Omega} + \frac{1}{2.6\ k\Omega} = 0.94\ k\Omega </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | So | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R = 1.06\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | And | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>C_2 \gg \frac{1}{(2\pi\ 20)\ R_L} = \frac{1}{(2\pi\ 20)\ 1.06\ k\Omega} = 7.5\times10^{-6} F</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To be safe I have choose the following values for <math>C_1</math> and <math>C_2</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>C_1 = C_2 = 100\ \mu F</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==Measure all DC voltages in the circuit and compare with the predicted values.(10 pnts)== | ==Measure all DC voltages in the circuit and compare with the predicted values.(10 pnts)== | ||
| Line 154: | Line 202: | ||
<math>I_1 = (603 \pm 1)\ uA</math> | <math>I_1 = (603 \pm 1)\ uA</math> | ||
| − | ==Measure the voltage gain <math> | + | ==Measure the voltage gain <math>A_{\nu}</math> as a function of frequency and compare to the theoretical value.(10 pnts)== |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In the table below are my input and output voltage measurements and voltage gain calculation. Here the <math>V_{in}</math> is the peak-to-peak value of the input voltage, the <math>V_{out}</math> is the peak-to-peak value of the output voltage, and <math>A_{\nu} = \frac{V_{out}}{V_{in}}</math> is the voltage gaine. | ||
[[File:Table gain.png | 700 px]] | [[File:Table gain.png | 700 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | My theoretical voltage gain are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>A_{\nu} = \frac{\beta R_C}{R_{BE}}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here I do not really know the values of <math>R_{BE}</math>. But typically <math>R_C</math> and <math>R_{BE}</math> are the same order of magnitude so the approximate voltage gain are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>A_{\nu} \approx \beta = 173</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | As we can see from the table above my theoretical voltage gain are in good agreement with the measured ones in wide range of frequencies from the low frequency <math>f = 300\ Hz</math> up to high frequency <math>f = 200\ kHz</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The decreasing of measured gain in low frequencies can be explained from the fact that capacitors <math>C_1</math> and <math>C_2</math> actually form the high-pass filter for input and output AC signals. And because I have measured <math>V_{in}</math> before <math>C_1</math> and <math>V_{out}</math> after <math>C_2</math> that will drop down my measured gain at low frequencies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Curcuit06.png | 500 px ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
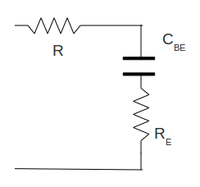
| + | The decreasing of measured gain at high frequency can be explain from the fact that the transistor have some nonzero capacitance value <math>C_{BE}</math>. So the transistor by itself will behave as low-pass filter. Because this <math>C_{BE}</math> capacitance should be small enough the breaking point frequency <math>\omega_B = \frac{1}{RC}</math> should be high enough. As the result we have the attenuation of measured voltage gain at high frequencies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Curcuit062.png | 200 px ]] | ||
==Measure <math>R_{in}</math> and <math>R_{out}</math> at about 1 kHz and compare to the theoretical value.(10 pnts)== | ==Measure <math>R_{in}</math> and <math>R_{out}</math> at about 1 kHz and compare to the theoretical value.(10 pnts)== | ||
| Line 164: | Line 237: | ||
| − | ===Input impedance <math>R_{in}</math> measurements=== | + | ===Input impedance <math>R_{in}</math> measurements and comparing with theory=== |
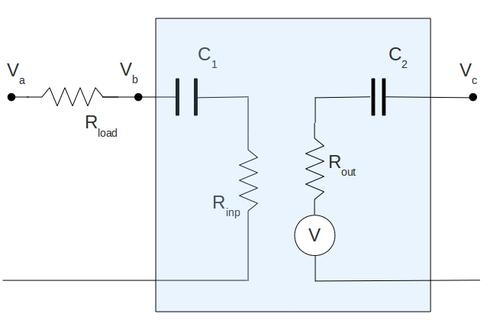
| − | To measure the input impedance of my amplifier I have set up the circulant below. Here I have attached the resistor <math>R_L</math> in-front of capacitor <math>C_1</math> and I replaced all my input internal resistor of amplifier by equivalent resistor <math>R_{inp}</math>. | + | To measure the input impedance of my amplifier I have set up the circulant below. Here I have attached the resistor <math>R_L</math> in-front of capacitor <math>C_1</math> and I replaced all my input internal resistor of amplifier by equivalent resistor <math>R_{inp}</math>. Here I have draw the capacitor <math>C_1</math> only for clearness and it does not included in calculation below. My input signal frequency is <math>1\ kHz</math> |
| Line 175: | Line 248: | ||
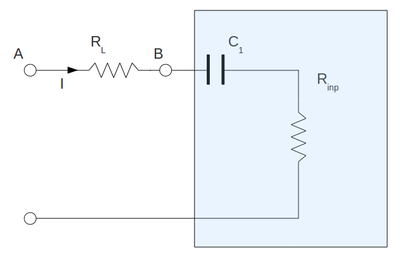
Using Ohm's Law: | Using Ohm's Law: | ||
| − | <math>I = \frac{V_B | + | <math>I = \frac{V_A-V_B}{R_L}</math> |
and | and | ||
| − | <math>R_{inp} = \frac{V_B}{I} = R_L\ \frac{V_B}{V_B | + | <math>R_{inp} = \frac{V_B}{I} = R_L\ \frac{V_B}{V_A-V_B}</math> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
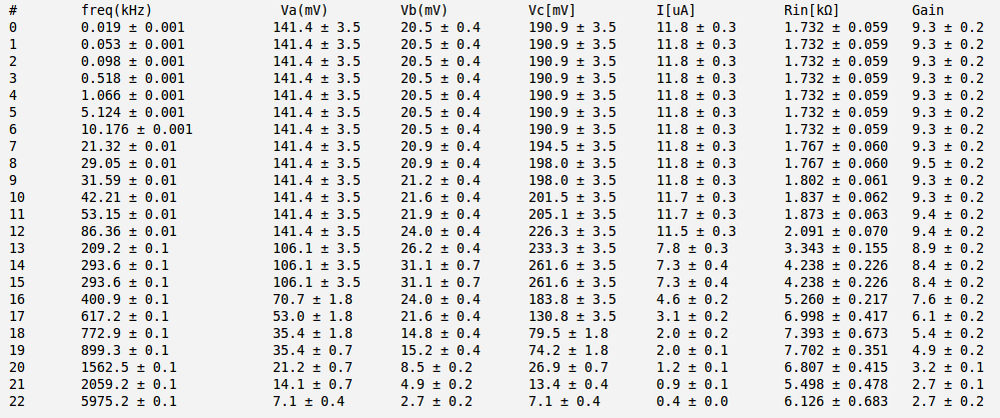
| + | Below is the table with my measurements and <math>R_{inp}</math> calculation. I did that calculation for several values of <math>R_L</math>. Here <math>V_A</math> and <math>V_B</math> are the RMS values. | ||
| + | |||
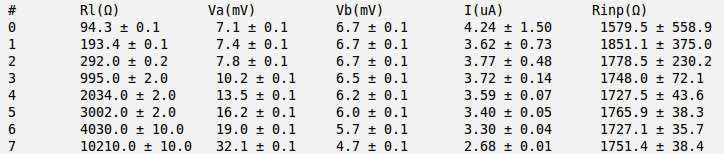
| + | [[File:Rinp table 03.png | 750px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The minimum error for <math>R_{inp}</math> I have for the case <math>R_L=4030\ \Omega</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | So my best estimate for <math>R_{inp}</math> is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{inp} = (1727.1 \pm 35.7)\ \Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The theoretical values of input impedance can be described using the so called <math>h</math> parameter as: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{in} \approx (h_{ie}||R_1||R_2)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> h_{ie} \cong \frac{\beta kT}{e I_C}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | or using <math>\beta \approx 173 </math>, <math>T = 300\ K</math> and <math>I_C = 2.5\ mA</math> | ||
| − | + | <math> h_{ie} = 1.79\ k\Omega</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | So, | |
| − | + | <math>(R_{in})_{theory} \approx (1.79\ k\Omega||2.00\ k\Omega||16.26\ k\Omega) \approx 0.89\ k\Omega</math> | |
| − | To measure the output impedance of my amplifier I have set up the circulant below. Here I have attached the resistor <math>R_L</math> after of capacitor <math>C_2</math> and I replaced all my output internal resistor of amplifier by equivalent resistor <math>R_{out}</math>. | + | |
| + | |||
| + | This result is in not really well agreement with my measured values of | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(R_{inp})_{exp} = (1727.1 \pm 35.7)\ \Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The discrepancy probably can be explained by approximate nature of the theoretical formula and maybe assumed values of temperature <math>T = 300\ K</math> which I do not really measured. Maybe my method of measuring input impedance was not good. Anyway this big discrepancy need more detailed study. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Output impedance <math>R_{out}</math> measurements and comparing with theory=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
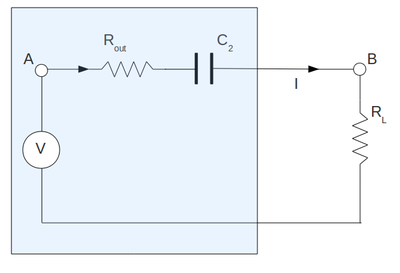
| + | To measure the output impedance of my amplifier I have set up the circulant below. Here I have attached the resistor <math>R_L</math> after of capacitor <math>C_2</math> and I replaced all my output internal resistor of amplifier by equivalent resistor <math>R_{out}</math>. Here I have draw the capacitor <math>C_2</math> only for clearness and it does not included in calculation below. | ||
| Line 210: | Line 318: | ||
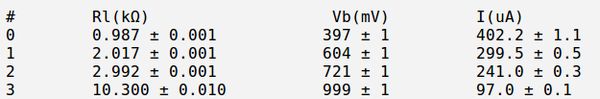
| − | Below is the table with my measurements and current calculation | + | Below is the table with my measurements and current calculation. Here <math>V_B</math> is the RMS values. |
[[File:Rout table.png | 600px]] | [[File:Rout table.png | 600px]] | ||
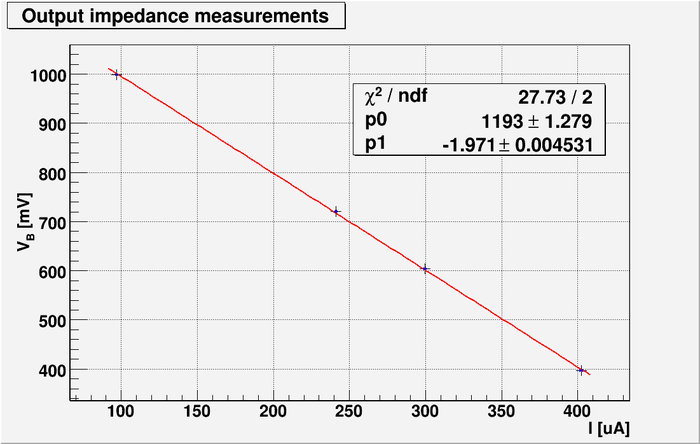
| − | And below is my plot output voltage <math>V_B<math> as function of current <math>I</math>: | + | And below is my plot of output voltage <math>V_B</math> as function of current <math>I</math>: |
| − | [[File:L14 outimpedance.png | | + | [[File:L14 outimpedance.png | 700px]] |
| − | The line equation is <math>V_B[mV]=p_0 + p_1\cdot I[\ | + | The line equation is <math>V_B[mV]=p_0[mV] + p_1\cdot I[\mu A] </math> |
| + | The slope of this line is <math>p_0=(1.971\pm 0.004)\ \frac{mV}{\mu A} = (1.971\pm 0.004)\ k\Omega</math>. | ||
| − | The | + | So my measured output impedance is: |
| + | |||
| + | <math> R_{out} = (1.971\pm 0.004)\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The theoretical values of output impedance can be described as: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{out} \approx \left(\frac{h_{ie}}{\Delta_e h}\right)||R_C</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | I do not really know here the <math>\Delta_e h</math> but assuming the values of <math>\Delta_e h \approx 2\cdot 10^{-2}</math> and using <math> h_{ie} = 1.79\ k\Omega</math> calculated above | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{out} \approx (89.5\ k\Omega)||R_C</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using the actual values of <math>R_C = 2\ k\Omega</math> we get finally for the theoretical values of output impedance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\left(R_{out}\right)_{theory} \approx (89.5\ k\Omega||2.0\ k\Omega) = 1.96 k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This theoretical values is in very well agreement with my measured values | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> \left(R_{out}\right)_{exp} = (1.971\pm 0.004)\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | that tell me that the method I have used to measure the output impedance is pretty good and accurate. | ||
==Measure <math>A_v</math> and <math>R_{in}</math> as a function of frequency with <math>C_E</math> removed.(10 pnts)== | ==Measure <math>A_v</math> and <math>R_{in}</math> as a function of frequency with <math>C_E</math> removed.(10 pnts)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To measure <math>A_v</math> and <math>R_{in}</math> as a function of frequency with <math>C_E</math> removed I have set up the following circuit: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Curcuit051.png | 500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Here the box represents the equivalent circuit for my amplifier (with removed <math>C_E</math>). Here I have draw the capacitor <math>C_1</math> and <math>C_2</math> only for clearness and it does not included in calculation below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The input impedance <math>R_{in}</math> is as before: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{inp} = R_{load}\ \frac{V_b}{V_a - V_b}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and the voltage gain <math>A_{\nu}</math> is as before | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>A_{\nu} =\frac{V_{out}}{V_{inp}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In the table below are presented my measurements and <math>R_{in}</math> and voltage gain <math>A_v</math> calculation. Here <math>V_A</math>, <math>V_B</math> and <math>V_C</math> are the RMS values. I have measured peak-to-peak values by oscilloscope and than convert them to RMS. It's why I have fractional values for voltage errors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Table rinp03.png | 1000px ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | As we can observe from the table above the measured voltage gain for the case with removed <math>C_E</math> is much less than the measured voltage gain values for the case with <math>C_E</math>. It's in agreement with the main function of emitter conductance <math>C_E</math> to avoid decreasing the gain of amplifier. | ||
=Questions= | =Questions= | ||
| − | + | == Why does a flat load line produce a high voltage gain and a steep load line a high current gain? (10 pnts)== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | If we have a flat load line then by changing a little the input signal (so we will change the <math>I_B</math> and will move up or down in load line) we will change a lot of <math>V_{CE}</math>. As the result we have high voltage gain. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | If we have a steep load line then by changing a little the input signal (so we will change the <math>I_B</math> and will move up or down in load line) we will change a lot of <math>I_C</math>. As the result we have high current gain. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==What would be a good operating point an an <math>npn</math> common emitter amplifier used to amplify negative pulses?(10 pnts)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The operating point should be as higher as possible in the load line so we will have the freedom of moving down in the load line to amplify the negative pulses. But it still has to be in saturation region of transistor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | ==What will the values of <math>V_C</math>, <math>V_E</math> , and <math>I_C</math> be if the transistor burns out resulting in infinite resistance. Check with measurement.(10 pnts)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | With burned transistor (removed) I will end up with the DC following circuit: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:curcuit0723.png | 250 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | As we can easily see because we have the open loop there are no current in collector and emitter and all voltage <math>V_{bb}</math> will drop between collector and emitter. As the result: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_C = V_{bb} = 11\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_E = V_C - V_{CE} = (11 - 11)\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_C = 0\ A</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | My measured values are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_C = (11.00 \pm 0.01)\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_E = (0.0 \pm 0.0)\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_C = (0.0 \pm 0.0)\ A</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | that is in total agreement with my predicted values | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==What will the values of <math>V_C</math>, <math>V_E</math> , and <math>I_C</math> be if the transistor burns out resulting in near ZERO resistance (ie short). Check with measurement.(10 pnts)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | With burned transistor (with zero resistance) I will end up with the DC following circuit: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:curcuit0733.png | 250 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now we have the perfect voltage divider: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_C = V_E = \frac{(R_E||R_1)}{(R_E||R_1) + (R_C||R_2)}\cdot V_{bb}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_E||R_1 = \frac{R_E R_1}{R_E + R_1} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_C||R_2 = \frac{R_C R_2}{R_C + R_2} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and using my actual values of resistors | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_E = (200.0 \pm 1.0)\ \Omega</math> | ||
| + | <math>R_C = (2.002 \pm 0.001)\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | <math>R_1 = (2.004 \pm 0.001)\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | <math>R_2 = (16.26 \pm 0.01)\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | I end up with | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_E||R_1 = (0.1818 \pm 0.0009)\ k\Omega </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_C||R_2 = (1.7825 \pm 0.0002)\ k\Omega </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_C = V_E = \frac{(0.1818 \pm 0.0009)}{(0.1818 \pm 0.0009) + (1.7825 \pm 0.0002)}\cdot (11.00 \pm 0.01)\ V = (1.018 \pm 0.005)\ V </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_C = \frac{V_{bb}-V_E}{R_C} = \frac{(11.00\pm 0.01)V-(1.018 \pm 0.005)V}{(2.002 \pm 0.001)k\Omega} = (4.986 \pm 0.009)\ mA</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | My measured values are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_C = V_E = (1.021 \pm 0.001)\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_C = (5.00 \pm 0.01)\ mA</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | that is in total agreement with my predicted values | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Predict the change in the value of <math>R_{in}</math> if <math>I_D</math> is increased from 10 <math>I_B</math> to 50 <math>I_B</math>(10 pnts)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Taking my biased base current value calculated above <math>I_B = 14.4\ uA</math> my corresponded <math>I_D</math> are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(I_D)_1 = 10 \cdot 14.4\ uA= 144\ uA</math> | ||
| + | <math>(I_D)_2 = 50 \cdot 14.4\ uA = 720\ uA</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | My change in <math>V_B</math> becomes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(V_B)_1 = (I_D)_1 \cdot R_1 = (144\ uA \cdot 2\ k\Omega) = 0.288\ V</math> | ||
| + | <math>(V_B)_2 = (I_D)_1 \cdot R_1 = (720\ uA \cdot 2\ k\Omega) = 1.440\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and corresponding change in <math>V_E</math> becomes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(V_E)_1 = (V_B)_1 - V_{BE} = (0.288 - 0.68) = -0.392\ V</math> | ||
| + | <math>(V_E)_2 = (V_B)_2 - V_{BE} = (1.440 - 0.68) = 0.76\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Here I ended up with the negative <math>(V_B)_1</math> value that is impossible for my case. The point here that my <math>R_1</math> was calculated to be able to conduct current <math>I_D = 590\ uA \gg 14.4\ uA</math>. So the case of increasing <math>I_D</math> from 10 <math>I_B</math> to 50 <math>I_B</math> is just impossible for my circuit just because I can get so low <math>I_D = 10\ I_B</math> values. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To make some reasonable estimate I will pick up the change in <math>I_D</math> current from 40 <math>I_B</math> to 200 <math>I_B</math>, so my relative change is 5 times as before. Now I have: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(I_D)_1 = 40 \cdot 14.4\ uA = 576\ uA</math> | ||
| + | <math>(I_D)_2 = 200 \cdot 14.4\ uA = 2880\ uA</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | My change in <math>V_B</math> becomes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(V_B)_1 = (I_D)_1 \cdot R_1 = (576\ uA \cdot 2\ k\Omega) = 1.152\ V</math> | ||
| + | <math>(V_B)_2 = (I_D)_1 \cdot R_1 = (2880\ uA \cdot 2\ k\Omega) = 5.760\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and corresponding change in <math>V_E</math> becomes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(V_E)_1 = (V_B)_1 - V_{BE} = (1.152 - 0.68) = 0.472\ V</math> | ||
| + | <math>(V_E)_2 = (V_B)_2 - V_{BE} = (5.760 - 0.68) = 5.08\ V</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and the <math>I_E</math> current change: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(I_E)_1 = \frac{(V_E)_1}{R_E} = \frac{0.472\ V}{200\ \Omega} = 2.36\ mA</math> | ||
| + | <math>(I_E)_2 = \frac{(V_E)_1}{R_E} = \frac{5.08\ V}{200\ \Omega} = 25.4\ mA</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now I can use formula for transistor input impedance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> h_{ie} \cong \frac{\beta kT}{e I_C}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and because <math>I_E \approx I_C</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> (h_{ie})_1 \cong \frac{\beta kT}{e (I_C)_1} = 1.89\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | <math> (h_{ie})_2 \cong \frac{\beta kT}{e (I_C)_2} = 0.18\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now I can use formula for the amplifier input impedance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R_{in} \approx (h_{ie}||R_1||R_2)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | and using corresponding values of resistors I will end up with: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(R_{in})_1 \approx (1.89||2.0||16.26)\ k\Omega = 0.92\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | <math>(R_{in})_2 \approx (0.18||2.0||16.26)\ k\Omega = 0.16\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | So if I increase my <math>I_D</math> current from 40 <math>I_B</math> to 200 <math>I_B</math> I will decrease my amplifier input impedance from <math>0.92\ k\Omega</math> to <math>0.16\ k\Omega</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sketch the AC equivalent circuit of the common emitter amplifier.(10 pnts)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The point here is to remove the resistors <math>R_E</math> which is shorted out by capacitor <math>C_E</math> and remove all capacitors <math>C_1</math>, <math>C_2</math> and <math>C_E</math> which are have zero resistance for ac circuit. Also because <math>V_{bb}</math> terminal of power supply is also ac grounded we can combine the <math>R_1</math> and <math>R_2</math> into one resistor <math>(R1||R2)</math> and we can connect the resistor <math>R_C</math> to the ground. So the ac equivalent circuit of the common emitter amplifier becomes: | ||
| + | [[File:Circuit08.png || 400 px]] | ||
[https://wiki.iac.isu.edu/index.php/Electronics_RS Go Back to All Lab Reports] [[Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement]] | [https://wiki.iac.isu.edu/index.php/Electronics_RS Go Back to All Lab Reports] [[Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:16, 8 April 2011
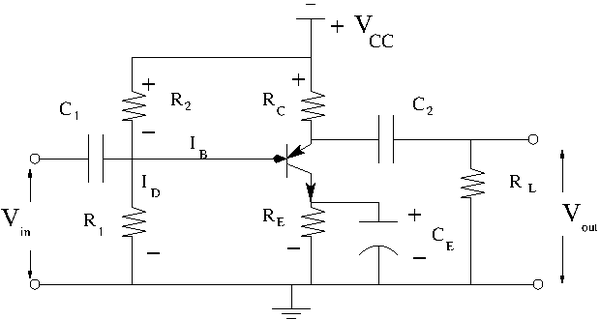
The Common Emitter Amplifier
Circuit
Construct the common emitter amplifier circuit below according to your type of emitter.
Calculate all the R and C values to use in the circuit such that
- a. Try and
- b. mA DC with no input signal
- c. V
- d. to prevent burnout
- e.
- f. mA
Let's , and .
The load line equation becomes:
About , and , , and see my calculations below.
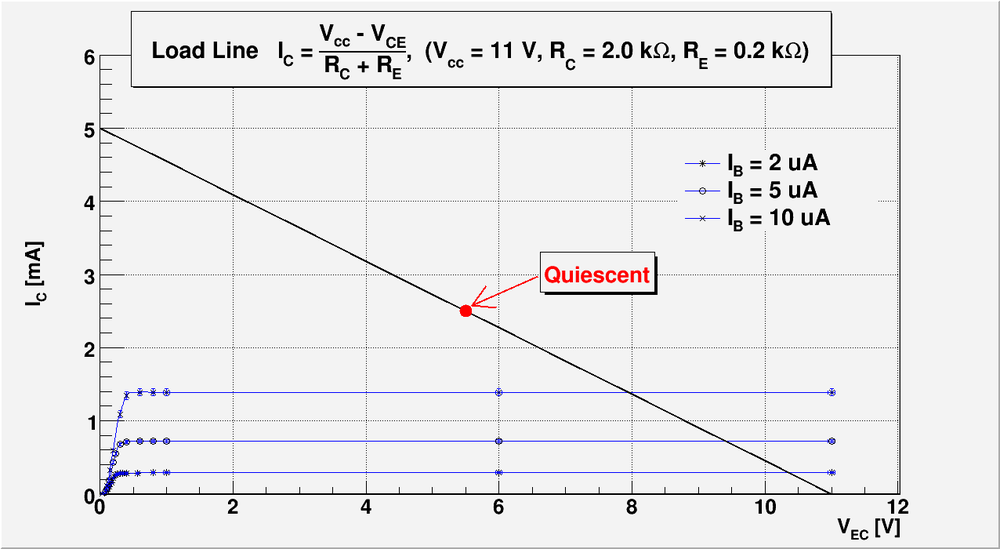
Draw a load line using the -vs- from the previous lab 13. Record the value of or .
On the plot below I overlay the output transistor lines (from the previous lab report #13) and the Load Line calculated above.
My reported values of in lab report #13 was . But this because we have used the approximation because small resistor value was used.
If we will do the accurate calculation of based on my lab report #13 measurements using exact formula:
we will end up with value of :
Set a DC operating point so it will amplify the input pulse given to you. Some of you will have sinusoidal pulses others will have positive or negative only pulses.
I will set up my operating point in the middle of the load line:
, .
Let's calculate all bias voltage needed to set up this operating point. Because the knowing of and is very important for this calculation I did the preliminary set up to measure this quantities. They are the only parameters which depends from transistor. I was able to find:
Now
To set up the above operating point we need to set up .
We have:
.
To get operating point independent of the transistor base current we want
Let's
So
And we can find from Kirchhoff Voltage Low:
.
and Kirchhoff Current Low:
So
I tried to adjust my calculation by varying the fee parameters and to end up with all my resistor values I can easily set up.
Now when we know all resistor values we are ready to calculate capacitor values.
1) To prevent decreasing in gain we need to make capacitance large enough so the will become small enough compared to to make AC signal grounded. Also note that the DC bias is not affected because will not pass the direct current.
So
I choose the electrolytic capacitor:
.
2) Now we need to block the amplifier from input and output signal to avoid change the DC bias. We can do it by placing the "blocking" capacitor, in series in-front and in-back of the amplifier. They both form the high-pass filter. And if we want to amplify the frequency more than we need to choose the breakpoint frequency to be:
For the output high-pass filter from the ac equivalent circuit we have where the resistance is the resistance of the output device. Let's
So
For the input high-pass filter from the ac equivalent circuit we have
So
And
To be safe I have choose the following values for and
Measure all DC voltages in the circuit and compare with the predicted values.(10 pnts)
My predicted DC voltages are: (from the calculation above):
My measured DC voltages are:
Here is very important to set up all resistor values as close as possible to my assumed values.
After many tries and errors I was able to end up with the following values of my resistors:
And my measurements of DC voltages looks like:
All my measurements are in agreement with each other within experimental errors.
I mean here that , and ,
Also all my predicted values are in agreement with my measured DC voltage values except of the fact that my measured instead of as I initially assumed. That gives me the correspondent corrections to . But if I will consider only the one significant sign all my predicted and measured DC voltage values are in total agreement.
Below are my current measurements which I did using millivoltmeter and which are also in agreement with each other and with all my previous calculation:
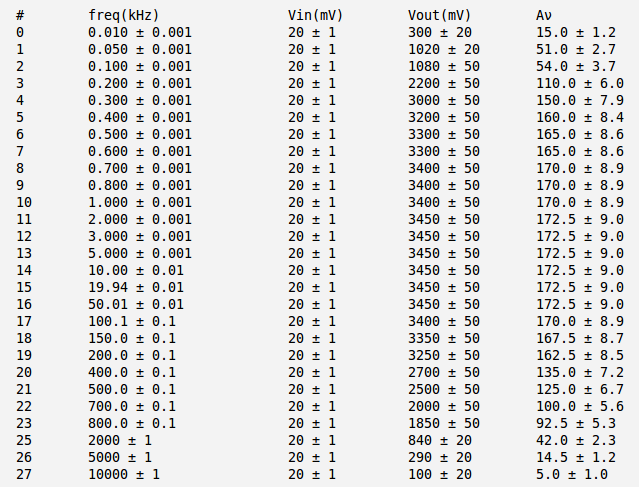
Measure the voltage gain as a function of frequency and compare to the theoretical value.(10 pnts)
In the table below are my input and output voltage measurements and voltage gain calculation. Here the is the peak-to-peak value of the input voltage, the is the peak-to-peak value of the output voltage, and is the voltage gaine.
My theoretical voltage gain are:
.
Here I do not really know the values of . But typically and are the same order of magnitude so the approximate voltage gain are:
.
As we can see from the table above my theoretical voltage gain are in good agreement with the measured ones in wide range of frequencies from the low frequency up to high frequency
The decreasing of measured gain in low frequencies can be explained from the fact that capacitors and actually form the high-pass filter for input and output AC signals. And because I have measured before and after that will drop down my measured gain at low frequencies.
The decreasing of measured gain at high frequency can be explain from the fact that the transistor have some nonzero capacitance value . So the transistor by itself will behave as low-pass filter. Because this capacitance should be small enough the breaking point frequency should be high enough. As the result we have the attenuation of measured voltage gain at high frequencies.
Measure and at about 1 kHz and compare to the theoretical value.(10 pnts)
How do you do this? Add resistor in front of which you vary to determine and then do a similar thing for except the variable reistor goes from to ground.
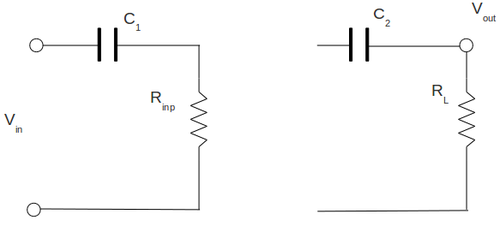
Input impedance measurements and comparing with theory
To measure the input impedance of my amplifier I have set up the circulant below. Here I have attached the resistor in-front of capacitor and I replaced all my input internal resistor of amplifier by equivalent resistor . Here I have draw the capacitor only for clearness and it does not included in calculation below. My input signal frequency is
Using Ohm's Law:
and
Below is the table with my measurements and calculation. I did that calculation for several values of . Here and are the RMS values.
The minimum error for I have for the case .
So my best estimate for is:
The theoretical values of input impedance can be described using the so called parameter as:
where
or using , and
So,
This result is in not really well agreement with my measured values of
The discrepancy probably can be explained by approximate nature of the theoretical formula and maybe assumed values of temperature which I do not really measured. Maybe my method of measuring input impedance was not good. Anyway this big discrepancy need more detailed study.
Output impedance measurements and comparing with theory
To measure the output impedance of my amplifier I have set up the circulant below. Here I have attached the resistor after of capacitor and I replaced all my output internal resistor of amplifier by equivalent resistor . Here I have draw the capacitor only for clearness and it does not included in calculation below.
Here to find out the output impedance we can use the battery method from lab#1. By Kirchoff voltage law:
and
So by graphing the current on the x-axis and the measured voltage on the y-axis for several values of the resistance
we can find the output internal impedance of our amplifier as the slope of the line
Below is the table with my measurements and current calculation. Here is the RMS values.
And below is my plot of output voltage as function of current :
The line equation is
The slope of this line is .
So my measured output impedance is:
The theoretical values of output impedance can be described as:
I do not really know here the but assuming the values of and using calculated above
Using the actual values of we get finally for the theoretical values of output impedance:
This theoretical values is in very well agreement with my measured values
that tell me that the method I have used to measure the output impedance is pretty good and accurate.
Measure and as a function of frequency with removed.(10 pnts)
To measure and as a function of frequency with removed I have set up the following circuit:
Here the box represents the equivalent circuit for my amplifier (with removed ). Here I have draw the capacitor and only for clearness and it does not included in calculation below.
The input impedance is as before:
and the voltage gain is as before
In the table below are presented my measurements and and voltage gain calculation. Here , and are the RMS values. I have measured peak-to-peak values by oscilloscope and than convert them to RMS. It's why I have fractional values for voltage errors.
As we can observe from the table above the measured voltage gain for the case with removed is much less than the measured voltage gain values for the case with . It's in agreement with the main function of emitter conductance to avoid decreasing the gain of amplifier.
Questions
Why does a flat load line produce a high voltage gain and a steep load line a high current gain? (10 pnts)
If we have a flat load line then by changing a little the input signal (so we will change the and will move up or down in load line) we will change a lot of . As the result we have high voltage gain.
If we have a steep load line then by changing a little the input signal (so we will change the and will move up or down in load line) we will change a lot of . As the result we have high current gain.
What would be a good operating point an an common emitter amplifier used to amplify negative pulses?(10 pnts)
The operating point should be as higher as possible in the load line so we will have the freedom of moving down in the load line to amplify the negative pulses. But it still has to be in saturation region of transistor.
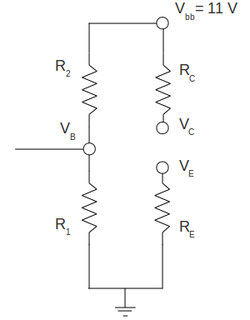
What will the values of , , and be if the transistor burns out resulting in infinite resistance. Check with measurement.(10 pnts)
With burned transistor (removed) I will end up with the DC following circuit:
As we can easily see because we have the open loop there are no current in collector and emitter and all voltage will drop between collector and emitter. As the result:
My measured values are:
that is in total agreement with my predicted values
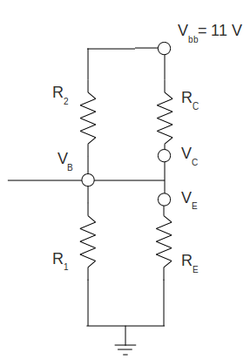
What will the values of , , and be if the transistor burns out resulting in near ZERO resistance (ie short). Check with measurement.(10 pnts)
With burned transistor (with zero resistance) I will end up with the DC following circuit:
Now we have the perfect voltage divider:
where
and using my actual values of resistors
I end up with
My measured values are:
that is in total agreement with my predicted values
Predict the change in the value of if is increased from 10 to 50 (10 pnts)
Taking my biased base current value calculated above my corresponded are:
My change in becomes:
and corresponding change in becomes:
Here I ended up with the negative value that is impossible for my case. The point here that my was calculated to be able to conduct current . So the case of increasing from 10 to 50 is just impossible for my circuit just because I can get so low values.
To make some reasonable estimate I will pick up the change in current from 40 to 200 , so my relative change is 5 times as before. Now I have:
My change in becomes:
and corresponding change in becomes:
and the current change:
Now I can use formula for transistor input impedance:
and because
Now I can use formula for the amplifier input impedance:
and using corresponding values of resistors I will end up with:
So if I increase my current from 40 to 200 I will decrease my amplifier input impedance from to
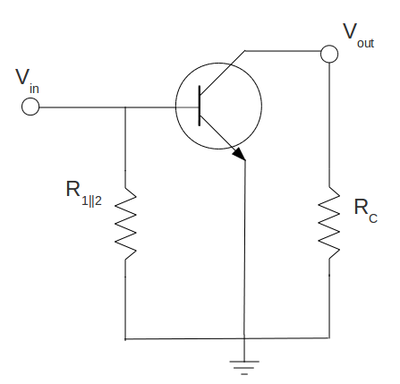
Sketch the AC equivalent circuit of the common emitter amplifier.(10 pnts)
The point here is to remove the resistors which is shorted out by capacitor and remove all capacitors , and which are have zero resistance for ac circuit. Also because terminal of power supply is also ac grounded we can combine the and into one resistor and we can connect the resistor to the ground. So the ac equivalent circuit of the common emitter amplifier becomes:
Go Back to All Lab Reports Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement