Difference between revisions of "Lab 9 RS"
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
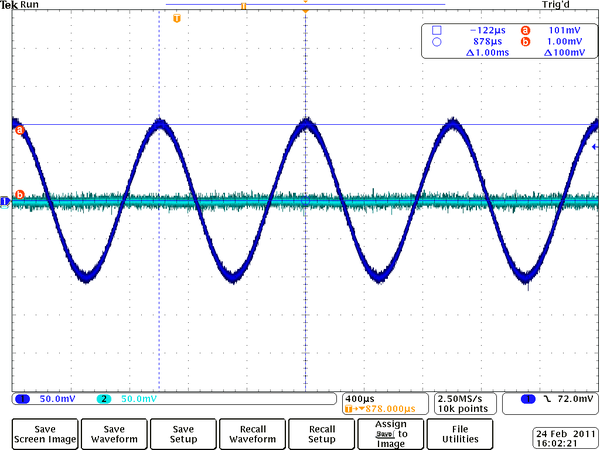
3.) Based on your observations using a oscilloscope, sketch the voltages <math>V_{in}</math> and <math>V_{out}</math> as a function of time. | 3.) Based on your observations using a oscilloscope, sketch the voltages <math>V_{in}</math> and <math>V_{out}</math> as a function of time. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Tek00034.png | 600 px]] |
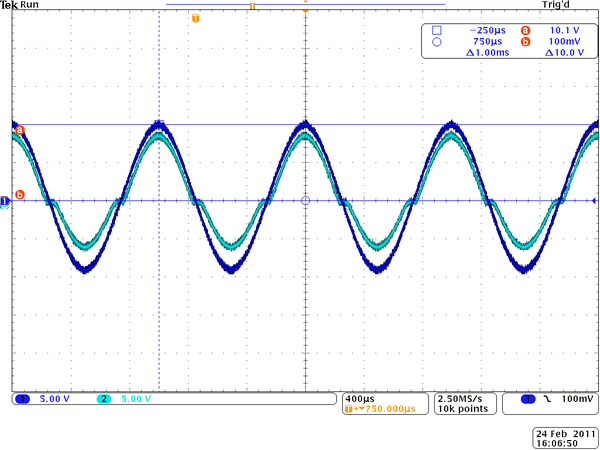
4.) Do another sketch for <math>V_0 </math> = 1.0 V and another for 10.0 V (DONT LET ANY SMOKE OUT!). (20 pnts) | 4.) Do another sketch for <math>V_0 </math> = 1.0 V and another for 10.0 V (DONT LET ANY SMOKE OUT!). (20 pnts) | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[FFile:Tek00035.png | 600 px]] |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Tek00036.png | 600 px]] |
| − | For the last sketch the output voltage is <math>V_{out} = 6\ V</math>. Let's estimate the power dissipated in resistor and diode. The current can be calculated by <math>I=\frac{V_{out}}{R}=\frac{6\ V}{ | + | For the last sketch the output voltage is <math>V_{out} = 8.6\ V</math>. Let's estimate the power dissipated in resistor and diode. The current can be calculated by <math>I=\frac{V_{out}}{R}=\frac{8.6\ V}{10.3 k\Omega} = 0.83\ mA</math>. |
| − | The resistor power is given by <math>P_R=I\cdot V_{out} = | + | The resistor power is given by <math>P_R=I\cdot V_{out} = 0.83\ mA \cdot 8.6\ V = 0.007\ W</math>. So we are OK here. |
| − | The diode power is given by <math>P_R=I\cdot V_{diode} = | + | The diode power is given by <math>P_R=I\cdot V_{diode} = 0.83\ mA \cdot (10 - 8.6)\ V = 0.001\ W</math>. So we are OK here as well. No any smoke out. |
= Differentiating Circuit with clipping= | = Differentiating Circuit with clipping= | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 24 February 2011
Lab 9: Diode Circuits
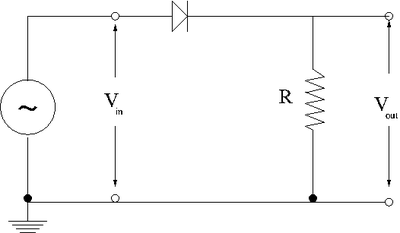
Clipping Circuit
1.) Construct the circuit shown below using a silicon diode.
I am going to use:
1) Zener diode 4.7 V 1N5230B-T
2) the resistor
2.) Use a sine wave generator to drive the circuit so where V and = 1kHz. (20 pnts)
3.) Based on your observations using a oscilloscope, sketch the voltages and as a function of time.
4.) Do another sketch for = 1.0 V and another for 10.0 V (DONT LET ANY SMOKE OUT!). (20 pnts)
For the last sketch the output voltage is . Let's estimate the power dissipated in resistor and diode. The current can be calculated by .
The resistor power is given by . So we are OK here.
The diode power is given by . So we are OK here as well. No any smoke out.
Differentiating Circuit with clipping
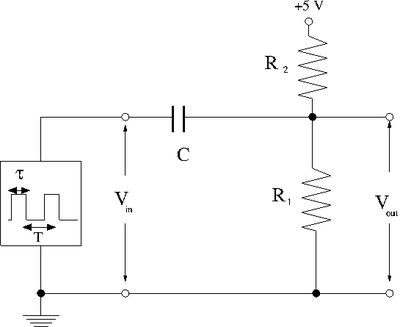
1) Construct the circuit below.
2) Select and such that the current from the +5V DC source is less than 1.0 mA and the DC voltage at is 3 V when there is no input pulse.
Because we want to keep the current below and using . Solving this inequality we get the first condition for and
Also because we want and using . Without any input pulse . Solving this simple equation we get the second condition for and
I am going to use and which satisfy both conditions above
3) Select a capacitor and a pulse width to form a differentiating circuit for the pulse from the signal generator. Hint: .
Taking and .
And choosing the the pulse width I will be able to make a good differentiator circuit.
4) plot and as a function of time using your scope observations. (20 pnts)
5) Now add the diode circuit from part 1 to prevent from rising above +5 V. Sketch the new circuit below.
6) plot and as a function of time with the diode circuit you added using your scope observations. (the diode should clip off positive spikes) (20 pnts)
Questions
- Explain your results in parts 1 & 2 in terms of the diode turn-on voltage. (20 pnts)
Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement Go Back to All Lab Reports