Difference between revisions of "JB Absolute theta"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Simulation == | == Simulation == | ||
| − | I performed an MCNP simulation of a D2O target subject to an 10.5 MeV end-point bremsstrahlung beam. A mock-up of our entire neutron detector array is included in the simulation. Detector physics is modeled by applying a detection threshold in terms of light output (MeVee), which is equal to the typical MeVee produced by 0.5 MeV neutrons within the scintillator. | + | I performed an MCNP simulation of a D2O target (axis length = 2"; dia. = 0.75") subject to an 10.5 MeV end-point bremsstrahlung beam. A mock-up of our entire neutron detector array is included in the simulation. Detector physics is modeled by applying a detection threshold in terms of light output (MeVee), which is equal to the typical MeVee produced by 0.5 MeV neutrons within the scintillator. |
| + | |||
| + | A Cf252 source was also simulated, allowing me to apply the exact same analysis technique to simulation and experimental data . | ||
| + | |||
| + | The plot below shows the relative distribution of neutron direction cosines w.r.t. the incident photon beam. These neutrons are not effected by scattering or detector geometry, since the direction cosine are taken right as neutrons are created. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:MCNPSimD20Theta abs.png|650px]] | ||
| − | |||
== Results == | == Results == | ||
Revision as of 07:13, 9 November 2017
Overview
Here I use neutron single events to measure the distribution of theta_abs, or the angle between an incident photon and a resultaning photo-neutron. The distribution of uncorrelated neutrons from the SF of californium 252 is used to "divide out" the effects of detector geometry, efficiency, drifts, ect. For D2O, the result is compared to an MCNP simulation which was built to model as many aspects of the experiment as possible.
Simulation
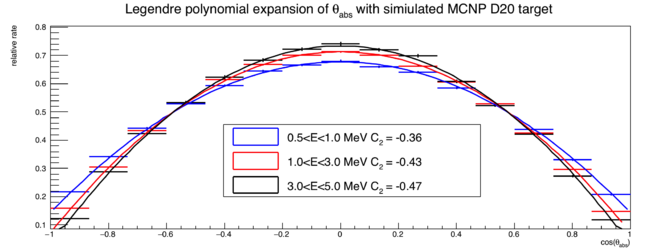
I performed an MCNP simulation of a D2O target (axis length = 2"; dia. = 0.75") subject to an 10.5 MeV end-point bremsstrahlung beam. A mock-up of our entire neutron detector array is included in the simulation. Detector physics is modeled by applying a detection threshold in terms of light output (MeVee), which is equal to the typical MeVee produced by 0.5 MeV neutrons within the scintillator.
A Cf252 source was also simulated, allowing me to apply the exact same analysis technique to simulation and experimental data .
The plot below shows the relative distribution of neutron direction cosines w.r.t. the incident photon beam. These neutrons are not effected by scattering or detector geometry, since the direction cosine are taken right as neutrons are created.
Results
MCNP-POLIMI
Below is an MCNP-POLIMI simulation of a cylindrical D20 target (axis length = 2"; dia. = 0.75") subject to a bremsstrahlung photon beam with an end point of 10.5MeV. The plot below shows the relative distribution of neutron direction cosines w.r.t. the incident photon beam. All neutrons are from the photodisintegration of D20 and the direction cosine is taken as neutrons exit the target geometry.