Difference between revisions of "Elastic scattering"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==Thorium== | ==Thorium== | ||
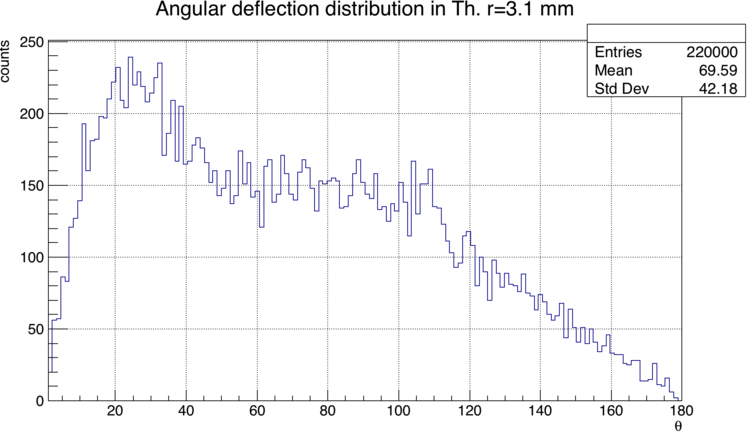
| − | Out of the neutrons that did scatter in the target, at least 96% did so at an angle greater than 10 degrees. | + | Out of the neutrons that did scatter in the target, at least 96% did so at an angle greater than 10 degrees. Below is the distribution of angle deflection for all the neutrons that did scatter. In this example, the target has a radius of 3 mm, and 8.2% of simulated neutrons did scatter in the target. |
[[File:Theta.png|750px]] | [[File:Theta.png|750px]] | ||
| − | + | Since the vast majority of neutrons do scatter (>96%) , my analysis simply considers any neutron that scatters as contaminated data. | |
Revision as of 01:28, 23 December 2015
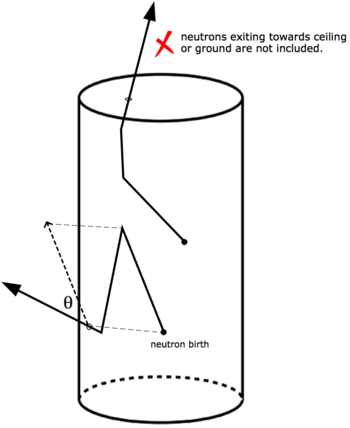
The simulation
Neutrons are generated uniformly within a cylindrical target with an energy sampled from a Watt fission spectrum. The angle between the direction that the neutron is traveling at birth and upon exiting the target volume is calculated. The figure below illustrates the angle that was calculated.
Neutrons that exit the target on a trajectory which will not intersect with a detector are not counted, e.g. neutrons going towards the ceiling or the ground.
Thorium
Out of the neutrons that did scatter in the target, at least 96% did so at an angle greater than 10 degrees. Below is the distribution of angle deflection for all the neutrons that did scatter. In this example, the target has a radius of 3 mm, and 8.2% of simulated neutrons did scatter in the target.
Since the vast majority of neutrons do scatter (>96%) , my analysis simply considers any neutron that scatters as contaminated data.
Go back JB Analysis